 PDF(1222 KB)
PDF(1222 KB)


Study on the behavior and blood index of TAUT transgenic rats
MAOLi-dong, FANWei-jia, LIXu, WANGChen, QIHao-ming, TONGHui-hui, XIAYi-ming, HUANGXiao-ling, ZHANGLing, CHENHe-hong, HUANGHui-ling
Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders ›› 2021, Vol. 4 ›› Issue (3) : 195-200.
 PDF(1222 KB)
PDF(1222 KB)
Abbreviation (ISO4): Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders
Editor in chief: Jun WANG
 PDF(1222 KB)
PDF(1222 KB)
Study on the behavior and blood index of TAUT transgenic rats
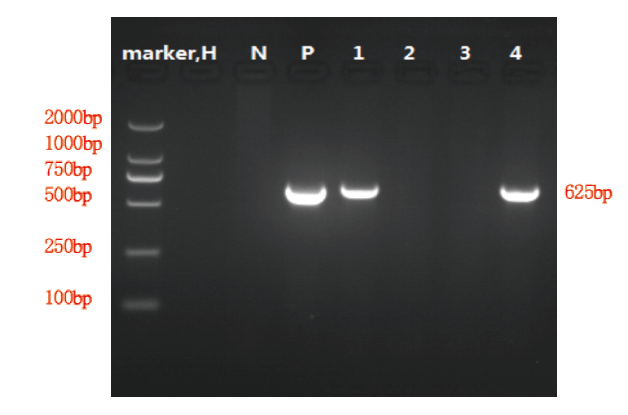
Objective: To study the changes of cognitive ability and blood parameters in a brain-specific transgenic rat model of taurine transporter (TAUT) (TauT-tg rats). Methods: TauT-tg rats and negative rats (NON-transgenic, NTG rats) were selected. The morris water maze test was used to detect their learning and cognitive ability, and heart blood was collected to detect the changes in total protein, albumin, and alkaline phosphatase. As well as the changes of 30 blood routine indexes such as white blood cell count, red blood cell count, hemoglobin and platelets, etc. The brain tissues to the cortex and hippocampus were observed under electron microscope. Results: Compared with NTG rats, there is no significant difference in the over all positioning navigation latency of TauT-tg rats, while the proportion of TauT-tg male rats in the platform quadrant is significantly shorter on the 5th day. The total protein, Albumin of TauT-tg female rats are lower than that of NTG female rats. There is no difference in alkaline phosphatase,while the indicators of male rats are not significantly different, the blood routine index of TauT-tg and NTG rats are not significant sexual differences, but within the same group, the white blood cell count and red blood cell count of male rats were significantly higher than that of female rats, and there was no significant difference in hemoglobin, platelet and other indicators. Analyzing the ultrastructure of neurons and organelles in TauT-tg rats by electron microscopy showed that there was no significant difference between TauT-tg and NTG rats. Conclusion: Transgenic TAUT may improve the cognitive ability of male rats and has no effect on general blood indicators of rats, but may cause malnutrition in female rats.
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
Hepatic ammonia handling was analyzed in taurine transporter (TauT) KO mice. Surprisingly, hyperammonemia was present at an age of 3 and 12 months despite normal tissue integrity. This was accompanied by cerebral RNA oxidation. As shown in liver perfusion experiments, glutamine production from ammonia was diminished in TauT KO mice, whereas urea production was not affected. In livers from 3-month-old TauT KO mice protein expression and activity of glutamine synthetase (GS) were unaffected, whereas the ammonia-transporting RhBG protein was down-regulated by about 50%. Double reciprocal plot analysis of glutamine synthesis versus perivenous ammonia concentration revealed that TauT KO had no effect on the capacity of glutamine formation in 3-month-old mice, but doubled the ammonia concentration required for half-maximal glutamine synthesis. Since hepatic RhBG expression is restricted to GS-expressing hepatocytes, the findings suggest that an impaired ammonia transport into these cells impairs glutamine synthesis. In livers from 12-, but not 3-month-old TauT KO mice, RhBG expression was not affected, surrogate markers for oxidative stress were strongly up-regulated, and GS activity was decreased by 40% due to an inactivating tyrosine nitration. This was also reflected by kinetic analyses in perfused liver, which showed a decreased glutamine synthesizing capacity by 43% and a largely unaffected ammonia concentration dependence. It is concluded that TauT deficiency triggers hyperammonemia through impaired hepatic glutamine synthesis due to an impaired ammonia transport via RhBG at 3 months and a tyrosine nitration-dependent inactivation of GS in 12-month-old TauT KO mice.
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
齐浩铭, 仝慧慧, 范维佳. TauT 转基因大鼠的构建及鉴定[J]. 天津医科大学学报. 2020; 26(1):1-7.
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
张建国, 孟凡刚, 刘阿力. 伽玛刀照射正常大鼠海马组织形态学结构的变化[J]. 中国微侵袭神经外科杂志. 2007; 12(3):129-131.
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
赵毓梅, 郑定仙, 黄业宇. SD大鼠血常规,血液生化指标、脏体比正常参考值范围研究[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志. 2002; 12(2):165-7.
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |