

Abbreviation (ISO4): Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders
Editor in chief: Jun WANG
Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders >
Application value of Stroop test in the evaluation of cognitive function in asymptomatic cerebral infarction
Received date: 2021-08-02
Revised date: 2021-09-15
Online published: 2021-12-25
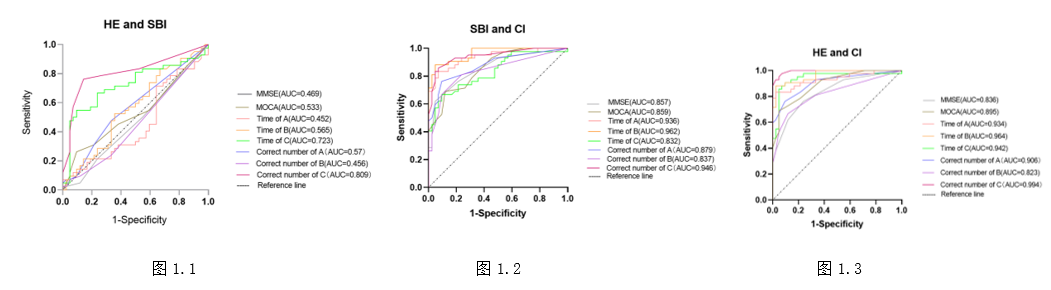
Objective: To compare the application value of MMSE, MoCA and modified Version of Stroop in the evaluation of cognitive function in patients with silent brain infarction (SBI). Methods: A total of 126 subjects (normal group, SBI group and cerebral infarction group 42 in each group) were selected from outpatient or inpatient department of neurology, 986 Hospital of Air Force from December 2019 to January 2021. After completing MMSE, MoCA and C-StroOP, ROC curves of each group were compared. Results: MMSE, MOCA score and the correct number of C-Stroop in normal group and SBI group were significantly lower than those in cerebral infarction group (P < 0.01), and the time of C-stroop was significantly increased (P < 0.01). There were no significant differences in MMSE and MOCA scores between normal group and SBI group (P > 0.05), the correct number of C-Stroop was significantly lower than that of SBI group (P < 0.01), and c-Stroop time was significantly increased (P < 0.01). All the three tests showed good differentiation between SBI and cerebral infarction group, normal population and cerebral infarction group (area under ROC was greater than 0.8). The sensitivity, specificity and area under curve (AUC) of C-Stroop were significantly better than those of MMSE and MoCA scores,MMSE score (0.024, 1, 0.469), MoCA score (0.262, 0.905, 0.533), correct number of C-Stroop task C (0.762, 0.857, 0.809) and time consuming (0.548, 0.905, 0.723). The truncation value of correct number pairs of C-stroop task was 21.5 (AUC=0.809), 14.5 (AUC=0.946) and 16.5 (AUC=0.994) for SBI and cerebral infarction patients. The truncation value of C-stroop t ask C time between normal subjects and SBI was 38.1515 (AUC=0.723), the truncation value between SBI and cerebral infarction group was 42.692 (AUC=0.832), and the truncation value between normal subjects and cerebral infarction was 39.0075 (AUC=0.942). Conclusions: C-Stroop has higher sensitivity and specificity than MMSE and MoCA in the evaluation of cognitive function in SBI patients, and is recommended for the evaluation and rapid screening of cognitive function in SBI patients.
Key words: asymptomatic cerebral infarction; The Stroop test; MMSE; MoCA; Cognitive function
BAI Qiu-ju , HU Jun , ZHANG Lin-jing , CHEN Yu , ZHANG Yan-hai , WANG Xian-chan , CHI Li-yi . Application value of Stroop test in the evaluation of cognitive function in asymptomatic cerebral infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders, 2021 , 4(4) : 269 -274 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-5516.2021.04.003
表1 3组人群基线资料比较Tab. 1 Comparison of baseline data among 3 groups |
| 组别 | 正常人 | 无症状脑梗死 | 脑梗死 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 年龄 | 51.88±5.00 | 52.40±7.20 | 53.71±12.00 | >0.05 |
| 性别(男/女) | 21/21 | 22/20 | 20/22 | >0.05 |
| 受教育年限 | 15.67±2.23 | 11.24±2.25 | 11.33±5.00 | >0.05 |
表2 正常人群、SBI、脑梗死组人群间MMSE总分、MoCA总分及C-Stroop结果对比Tab.2 Comparison of MMSE total score, MoCA total score and C-Stroop results among among different groups |
| 项目 | MMSE | MOCA | 任务A用时 | 任务B用时 | 任务C用时 | 任务A正确数 | 任务B正确数 | 任务C正确数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常组 | 29 (28.75~30) | 27 (26~29) | 30.1255 (26.93475~32.651) | 26.78 (24.67625~29.769) | 32.592 (29.94375~36.2225) | 24(23~24) | 24 (23~24) | 23 (22~24) |
| 无症状脑梗死组 | 29.5 (29~30) | 27 (24~29) | 27.996 (27.136~31.4735) | 27.576 (25.559~29.923) | 38.6535 (32.66~41.13075) | 24 (22~24) | 24 (23.75~24) | 20 (17~21.25) |
| 脑梗死组 | 27 (23~28.25) | 22 (15~25) | 42.453 (38.749~46.77825) | 38.974 (35.46575~43.9695) | 45.5045 (40.6965~52.15675) | 17.5 (11.75~21.25) | 21 (11~23) | 7 (3~11.25) |
| χ2 | 42.819 | 48.182 | 63.333 | 71.997 | 58.504 | 56.68 | 43.612 | 87.073 |
| p | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
表3 3组人群MMSE总分、MoCA总分及C-Stroop结果两两比较(χ 2/P )Tab.3 Pair comparison of MMSE total score, MoCA total score and C-Stroop results among the three groups(χ 2/P ) |
| 组别 | 正常组和无症状脑梗死组 | 无症状脑梗死组和脑梗死组 | 正常组和脑梗死组 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMSE | 0.20 | >0.05 | 34.57 | <0.05 | 29.46 | <0.05 |
| MoCA | 0.29 | >0.05 | 32.75 | <0.05 | 39.23 | <0.05 |
| 任务A用时 | 0.27 | >0.05 | 50.90 | <0.05 | 43.77 | <0.05 |
| 任务B用时 | 0.49 | >0.05 | 48.66 | <0.05 | 58.91 | <0.05 |
| 任务C用时 | 8.57 | <0.05 | 21.70 | <0.05 | 57.55 | <0.05 |
| 任务A正确数 | 0.85 | >0.05 | 36.14 | <0.05 | 48.04 | <0.05 |
| 任务B正确数 | 0.26 | >0.05 | 128.24 | <0.05 | 140.14 | <0.05 |
| 任务C正确数 | 12.50 | <0.05 | 32.61 | <0.05 | 85.50 | <0.05 |
表4 3组人群MMSE总分、MoCA总分、C-Stroop各指标约登指数分析Tab.4 Analysis of MMSE total score, MoCA total score and C-Stroop yoden index of the three groups |
| 组别 | 测试项目 | 界值 | 灵敏度 | 特异度度 | 最大约登指数 | 曲线下面积 | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 正常组和无症状脑梗死组 | MMSE | 25.5 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.024 | 0.469 | >0.05 |
| MoCA | 24.5 | 0.262 | 0.905 | 0.167 | 0.533 | >0.05 | |
| 任务A用时 | 27.611 | 0.714 | 0.357 | 0.071 | 0.452 | >0.05 | |
| 任务B用时 | 24.965 | 0.833 | 0.333 | 0.166 | 0.565 | >0.05 | |
| 任务C用时 | 38.1515 | 0.548 | 0.905 | 0.453 | 0.723 | <0.05 | |
| 任务A正确数 | 23.5 | 0.476 | 0.667 | 0.143 | 0.57 | >0.05 | |
| 任务B正确数 | 19 | 0.024 | 1 | 0.024 | 0.456 | >0.05 | |
| 任务C正确数 | 21.5 | 0.762 | 0.857 | 0.619 | 0.809 | <0.05 | |
| 无症状脑梗死组和脑梗死组 | MMSE | 27.5 | 0.619 | 0.952 | 0.571 | 0.857 | <0.05 |
| MoCA | 26.5 | 0.929 | 0.548 | 0.477 | 0.859 | <0.05 | |
| 任务A用时 | 37.001 | 0.833 | 0.929 | 0.762 | 0.936 | <0.05 | |
| 任务B用时 | 32.88 | 0.881 | 0.952 | 0.833 | 0.962 | <0.05 | |
| 任务C用时 | 42.692 | 0.667 | 0.905 | 0.572 | 0.832 | <0.05 | |
| 任务A正确数 | 21.5 | 0.762 | 0.905 | 0.667 | 0.879 | <0.05 | |
| 任务B正确数 | 23.5 | 0.81 | 0.762 | 0.572 | 0.837 | <0.05 | |
| 任务C正确数 | 14.5 | 0.857 | 0.929 | 0.786 | 0.946 | <0.05 | |
| 正常组和脑梗死组 | MMSE | 28.5 | 0.762 | 0.762 | 0.524 | 0.836 | <0.05 |
| MoCA | 24.5 | 0.714 | 0.905 | 0.619 | 0.895 | <0.05 | |
| 任务A用时 | 37.056 | 0.833 | 0.976 | 0.809 | 0.934 | <0.05 | |
| 任务B用时 | 32.836 | 0.881 | 0.976 | 0.857 | 0.964 | <0.05 | |
| 任务C用时 | 39.0075 | 0.857 | 0.952 | 0.809 | 0.942 | <0.05 | |
| 任务A正确数 | 21.5 | 0.762 | 0.905 | 0.667 | 0.906 | <0.05 | |
| 任务B正确数 | 22.5 | 0.667 | 0.881 | 0.548 | 0.823 | <0.05 | |
| 任务C正确数 | 16.5 | 0.929 | 0.976 | 0.905 | 0.994 | <0.05 |
图1 3种测试ROC曲线分析Fig. 1 ROC curve analysis for three tests Note: |
| [1] |
中华医学会神经病学分会, 中华医学会神经病学分会脑血管病学组. 中国无症状脑梗死诊治共识[J]. 中华神经科杂志, 2018, 51(9): 692-698.
|
| [2] |
飞行人员无症状脑梗死的诊断和飞行风险评估中国专家共识组. 飞行人员无症状脑梗死的诊断和飞行风险评估中国专家共识[J]. 《中华航空航天医学杂志》, 2016, 27(4): 245-252.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南写作组, 中国医师协会神经内科医师分会认知障碍疾病专业委员会. 2018 中国痴呆与认知障碍诊治指南(三):痴呆的认知和功能评估[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2018, 98(15):1125-1129.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
李晨, 胡义芳, 薄茂林, 等. 静止性脑梗死患者的元认知特征[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2021, 24(2): 148-153.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
喻锦成, 陈涛, 文国强, 等. 无症状性脑梗死认知功能的Stroop测验和TCD研究[J]. 海南医学, 2013,(5):27-29.
|
| [19] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |