

Abbreviation (ISO4): Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders
Editor in chief: Jun WANG
Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders >
Clinical and imaging characteristics of 4 patients with primary progressive aphasia
Received date: 2021-04-23
Revised date: 2021-06-01
Online published: 2021-09-25
objective: To analyze the cognitive, linguistic, psychobehavioral symptoms and imaging characteristics of patients with primary progressive aphasia (PPA). Methods: Of 4 patients diagnosed as PPA in the Memory Clinic of Tianjin Huanhu Hospital between April 2014 and March 2018, 1 patient with logopenic progressive aphasia(lvPPA),1 patient with progressive nonfluent aphasia (PNFA), 2 patients with semantic dementia(SD) were identified. Clinical data of the patients were collected. Cognitive function was measured by the Mini-Mental State Examination, Montreal Cognitive Assessment, Clinical Dementia Rating and China Rehabilitation Research Center Aphasia Examination. Also measured by NPI and HAMD depression scale. Brain magnetic resonance imaging was conducted to evaluate the cortex atrophy and medial temporal lobe atrophy. The 18F-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission tomography (18F-FDG-PET)and Pittsburg Compound B (PiB)PET cerebral imaging were performed in patients with atypical clinical and MRI demonstrations. Results: Among the 4 patients, 3 were male and 1 was female. The onset age was 58~71 years old, and the duration was 1~5 years. All 4 cases were right-handed. All the 4 patients had impaired memory and recall ability, repetitive language disorder and fluency of speech. LvPPA patients is characterized by difficulty in word extraction, naming and retelling, and difficulty in understanding complex sentences. Cognitive impairment progresses rapidly, and the activity of daily living is quickly impaired. Manifests as tension, irritability and fatigue. Head MRI showed bilateral parietal atrophy. PiB-PET shows amyloid deposits. FDG-PET showed decreased metabolism in bilateral temporo-parietal junction, bilateral precuneus and right frontal lobe. The early symptoms of PNFA patients are mainly verbal fluency, speech loss, and language clumsiness. It is difficult to repeat the sentence. The activity of daily living has less impact. The HAMD depression scale showed poor self-awareness. Head MRI showed atrophy of the frontotemporal lobe on the left.FDG-PET showed decreased metabolism in bilateral medial frontal, lateral, bilateral anterior cingulate, bilateral lateral temporal, left medial temporal, bilateral insula and bilateral caudate nucleus, and leftthalamus. The early main symptoms of SD patients are difficulty naming, poor comprehension and difficulty in finding words. The sentence retelling is poor, serious people can not read aloud or transcribe; Picture description and dictation are difficult. The NPI and HAMD scales showed depressive mood, anorexia and sleep disturbance. Head MRI showed bilateral frontal, parietal lobe, left temporal lobe atrophy. FDG-PET showed decreased metabolism of bilateral medial frontal, lateral, bilateral insula, left inner temporal, lateral and left caudate nuclei. Conclusion: PPA patients have different early cognitive,language disorders and mental and behavior disorder due to their anatomical basis. A detailed cognitive,language assessment and neuropsychiatric inventory questionnaire combined with head MRI and FDG-PET can help to identify the diagnosis early.
Key words: primary progressive aphasia; Dementia; Clinical neuroimage
ZHANG Miao , ZHANG Hui-hong , CAI Li , ZHOU Yu-ying . Clinical and imaging characteristics of 4 patients with primary progressive aphasia[J]. Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders, 2021 , 4(3) : 201 -205 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-5516.2021.03.006
表1 4例患者一般情况比较Tab. 1 The general conditions of 4 patients were compared |
| 学历 | MMSE评分 (分) | MOCA评分 (分) | ADL评分 (分) | 画钟试验 (分) | CDR (分) | HIS评分 (分) | NPI评分 患者 护理者 (分) (分) | Hamilton 抑郁(分) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 例1(1) | 大学 | 23 | 15 | 22 | 2 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 4 |
| 例1(2) | 19 | 12 | 26 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 4 | |
| 例2 | 大学 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 4 | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 |
| 例3 | 小学 | 23 | 16 | 21 | 3 | 0.5 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 5 |
| 例4 | 大学 | 23 | 14 | 24 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 7 |
图1 患者头颅MRI成像。AD: lvPPA患者双侧顶叶萎缩,颞叶内侧萎缩。BE: PNFA患者左侧为著的额颞叶萎缩,颞叶内侧萎缩。CF: SD患者左侧颞叶萎缩,脑室扩大。Fig.1 MRI of the patient's head. A D: The patient of lvPPA had bilateral parietal lobe atrophy and medial temporal lobe atrophy. B E:The patient of PNFA had frontal temporal lobe atrophy on the left and medial temporal lobe atrophy. C F:The patient of SD had left temporal lobe atrophy and enlarged ventricles. |
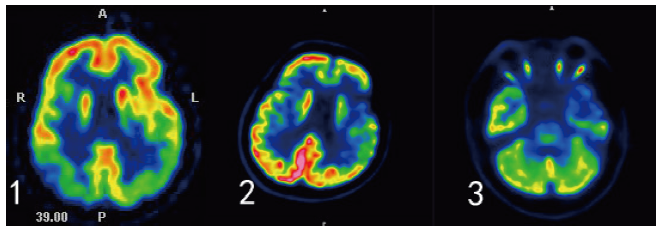
图2 18 F-FDG-PET检查所示。1:lvPPA患者FDG-PET显示双侧颞-顶联合区、双侧楔前叶及右侧额叶代谢减低。2:PNFA患者FDG-PET显示双额内、外侧、双前扣带回、双颞外侧、左颞内侧、双岛叶及双尾状核、左丘脑代谢减低。3: SD患者FDG-PET显示双岛叶、左颞内、外侧代谢减低。Fig.2 18 F-FDG-PET shows. 1: The patient of lvPPA displays decreased metabolism in bilateral temporo-parietal junction, bilateral precuneus, and right frontal lobe. 2: The patient of PNFA shows decreased metabolism in the medial, lateral, anterior cingulate gyrus, lateral temporalis, medial temporalis, insula, caudate nucleus and left thalamus. 3: The patient of SD displays decreased metabolism in both insula, left temporal and lateral lobes. |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |