

Abbreviation (ISO4): Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders
Editor in chief: Jun WANG
Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders >
Cell to cell transmission of misfolded tau protein in neurodegenerative diseases and possible therapeutic strategies
Received date: 2021-01-10
Revised date: 2021-03-15
Online published: 2021-06-25
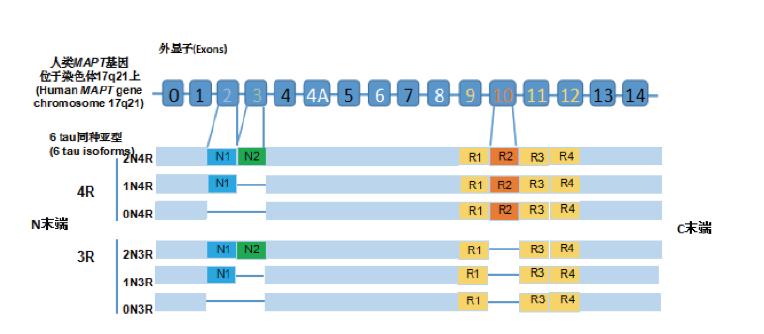
The aggregation of misfolded pathogenic proteins in the brain is a common characteristic in most neurodegenerative diseases, such as misfolded pathogenic Aβ peptides and hyper-phosphorylated tau proteins in Alzheimer's diseases (AD), α-synuclein in Parkinson's diseases (PD), TDP43 proteins in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal degeneration (FTD), and polyQs in Huntington's disease (HD). These different misfolded pathogenic proteins have been reported to be transmitted from one brain area to broad brain regions and cause neuronal dysfunction directly or indirectly. In this review, the tau protein is used as an example to review mechanisms of aggregation, transmission and possible therapeutic strategies for neurodegenerative diseases. The potential therapeutic strategies in the treatment of these tau neurodegenerative diseases are proposed. Hope this review can help clinic doctors and research scientists easily to understand the tauopathy on basic science and recent research progress in a short time.
ZHANG Bin , ZHANG Ying , WANG Jun . Cell to cell transmission of misfolded tau protein in neurodegenerative diseases and possible therapeutic strategies[J]. Chinese Journal of Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders, 2021 , 4(2) : 145 -155 . DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-5516.2021.02.013
表1 大量的神经变性疾病含有tau蛋白病理改变Tab.1 Many neurodegenerative diseases contain tauopathies |
| 神经变性疾病(中文) | 神经变性疾病(英文) |
|---|---|
| 阿尔茨海默病 | Alzheimer's disease (AD) |
| 皮克氏病 | Pick's disease (PiD) |
| 皮质基底节变性 | Cortical basal degeneration (CBD) |
| 进行性核上性麻痹 | Progressive supernuclear palsy (PSP) |
| 帕金森氏病 | Parkinson's disease (PD) |
| 嗜银颗粒病 | Argyrophilic grain disease (AGD) |
| 特发性脑干神经元染色 质溶解 | Idiopathic brainstem neuronal chromatolysis (IBNC) |
| 拳击手痴呆症 | Dementia pugilistica |
| 唐氏综合症 | Down syndrome |
| 朊病毒疾病 | Prion diseases |
| 肌萎缩侧索硬化症/帕金森氏症 - 痴呆综合征 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex(ALS/PDC) |
| 弥漫性神经纤维缠结伴钙化 | Diffuse neurofibrilary tangles with calcification |
| 染色体-17相关的额颞叶痴呆/帕金森氏综合征(FTDP-17) | Frontotemporal dementia/parkinsonism linked to chromosome-17 (FTDP-17) |
| 亚急性硬化性全脑炎 | Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis |
| 神经纤维缠结型阿尔茨海默病 | Tangle-predominant Alzheimer's disease |
表2 主要tau病变疾病的特点Tab. 2 Main characteristics of tauopathies |
| 疾病名称 | tau的类型 | tau病变 | 其它病变 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 阿尔茨海默病 | Alzheimer's disease (AD) | 3R & 4R | 双股螺旋丝 paired, helical twisted filaments (神经原纤维缠结, neurofibrillary tangles, NFT) | Beta-淀粉样蛋白 (老年斑, senile plaques) |
| 皮克氏病 | Pick's disease (PiD) | 3R | 随机丝 random filaments (Pick小体, Pick's body) | |
| 皮质基底节变性 | Cortical basal degeneration (CBD) | 4R | 丝 filaments (白质神经纤维索 white matter threads, 星形胶质细胞斑块 astrocytic plaques, 气球状神经元 ballooned neurons) | |
| 进行性核上性麻痹 | Progressive supernuclear palsy (PSP) | 4R | 直丝 straight filaments (球状神经原纤维缠结 global NFT, 簇绒星形胶质细胞 tufted astrocyte, 少突胶质细胞的盘绕小体, oligodendrocyte coil body) | |
| 帕金森氏病 | Parkinson's disease (PD) | 3R & 4R | 双股螺旋丝 Paired helical filaments | a突触核蛋白[路易体, Lewy bodies (LB), 路易神经纤维 Lewy nurites (LN)] |
| 嗜银颗粒病 | Argyrophilic grain disease (AGD) | 4R | 丰富的神经毡颗粒 abundant neuropil grains (tau) | |
| 特发性脑干神经元染色质溶解 | Idiopathic brainstem neuronal chromatolysis (IBNC) | 3R | 在神经元和胶质细胞中含有过度磷酸化tau病变 |
表3 不同神经变性疾病中不同病理蛋白质聚集体Tab.3 Various pathological protein aggregates in different neurodegenerative diseases |
| 病理蛋白液 | 聚集体 | 神经变性疾病 |
|---|---|---|
| tau蛋白 Beta-淀粉样蛋白 | 双股螺旋丝 paired, helical twisted filaments (神经原纤维缠结, neurofibrillary tangles, NFT) 老年斑, senile plaques | 阿尔茨海默病 Alzheimer's disease (AD) |
| tau 蛋白 | 球状神经原纤维缠结,簇状星形胶质,卷曲体 globose NFTs, tufted astroglia, coiled bodies | 进行性核上性麻痹 Supernuclear Progressive Pulsy (PSP) |
| tau 蛋白 | Pick's小体,tau阳性星形胶质细胞 Pick's body, tau possitive astroglia | 皮克氏病 Pick's disease (PiD) |
| a-突触核蛋白 a-Syneiclein, | 路易体, 路易神经纤维 Lewy bodies (LB), Lewy neurites (LN) | 帕金森病 Parkinson's disease |
| a-突触核蛋白 a-Syneiclein, | 路易体, 路易神经纤维 Lewy bodies (LB), Lewy neurites (LN) | 帕金森病伴痴呆 Parkinson's disease with dementia (PDD) |
| a-突触核蛋白 a-Syneiclein, | 路易体, 路易神经纤维 Lewy bodies (LB), Lewy neurites(LN) | 路易体痴呆 Dementia with lewy body (DLB) |
| TAR DNA结合蛋白 43 TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) | DNA结合蛋白包涵体43 TDP-43 inclusions | 额颞叶痴呆 Frontotemporal Dementia (FTLD) |
| TAR DNA结合蛋白 43 TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) | DNA结合蛋白包涵体43 DP-43 inclusions | 肌萎缩性侧索硬化症 Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) |
| 多聚谷氨酰胺 Polyglutamine aggragates (PolyQ) | Huntingtin inclusions 亨廷顿包涵体 | 亨廷顿病 Huntington's disease (HD) |
| 朊病毒 PrPc Prion | 海绵状改变, 朊病毒阳性染色 spongiform change, Prion positive staining | 克雅氏病 Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease (CJD) |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |