 PDF(30198 KB)
PDF(30198 KB)


High-Entropy Oxygen Evolution Catalysts: Mechanistic Analysis, Optimization Strategies, and Prospective Challenges
Shaofu Kuang, Xue Lu, Jianxing Wang, Hua Lin, Qing Li
Prog Chem ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11) : 1581-1603.
 PDF(30198 KB)
PDF(30198 KB)
 PDF(30198 KB)
PDF(30198 KB)
High-Entropy Oxygen Evolution Catalysts: Mechanistic Analysis, Optimization Strategies, and Prospective Challenges
Hydrogen production via water electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources represents a critical approach to addressing the dual challenges of energy and the environment. However, the practical implementationof this technology remains constrained by the sluggish kinetics of the anodic oxygen evolution reaction (OER). Recent advances in high-entropy materials (HEMs) with unique structural configurations and compositional tunability have demonstrated breakthrough capabilities in OER catalysis. Their near-continuous adsorption energy tunability across multi-dimensional landscapes enables surpassing the perforce ceilings of conventional single-/dual-component electrocatalysts. While substantial progress has been achieved in developing HEMs for OER catalysis, formidable scientific challenges persist regarding the intricate composition-structure-activity relationships in multi-component systems and unresolved mechanistic ambiguities governing catalytic synergies. This review systematically examines the fundamental mechanisms underlying the four-electron transfer process in OER, followed by a critical survey of recent breakthroughs in high-entropy alloys (HEAs), high-entropy oxides (HEOs), and high-entropy metal-organic frameworks (HEMOFs) for OER applications. By emphasizing three critical dimensions: atomic coordination environment modulation, electronic structure engineering, and surface adsorption energy optimization, we establish explicit correlations between compositional architecture, structural characteristics, and catalytic performance. This framework profoundly elucidates the synergistic catalytic mechanisms arising from multi-metallic active sites. Furthermore, we propose strategic optimization pathways through material design, defect engineering, and elemental regulation. The review concludes by discussing emerging challenges and future opportunities in this rapidly evolving field. This review can provide inspiration for the accurate design of high-entropy electrocatalysts, the atomic-level analysis of structure-activity relationships, and the regulation and optimization of catalytic performance.
Contents
1 Introduction
2 OER pathway
2.1 AEM
2.2 LOM
2.3 OPM
3 Research progress and bottlenecks of high‑entropy oxygen evolution catalytic materials
3.1 High‑entropy alloys
3.2 High‑entropy oxides
3.3 High‑entropy MOFs
3.4 Other high‑entropy compounds
4 Optimization strategies
4.1 Machine learning‑assisted design
4.2 Defect engineering
4.3 Element regulation
5 Conclusion and outlook
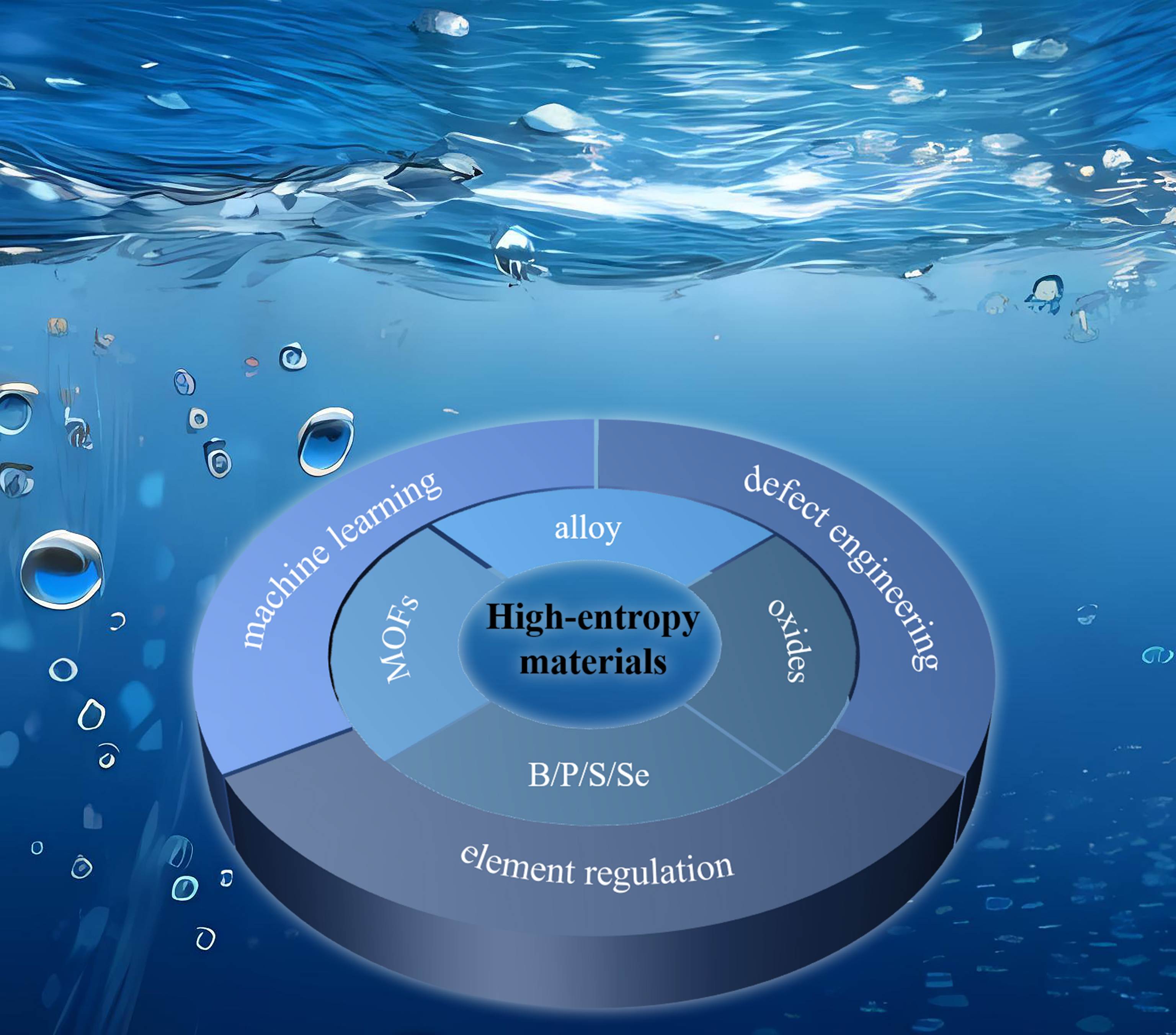
high-entropy materials / electrocatalysis / oxygen evolution reaction / optimization strategies
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
(薛世翔, 吴攀, 赵亮, 南艳丽, 雷琬莹. 化学进展, 2022, 34(12): 2686).
|
| [103] |
(周伶俐, 谢瑞刚, 王林江. 化学进展, 2019, 31(2/3): 275).
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [154] |
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
|
| [157] |
|
| [158] |
|
| [159] |
|
| [160] |
|
| [161] |
|
| [162] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |