 PDF(36153 KB)
PDF(36153 KB)


Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Microneedle System for Transdermal Drug Delivery
Wanping Zhang, Ningning Liu, Qianjie Zhang, Wen Jiang, Zixin Wang, Dongmei Zhang
Prog Chem ›› 2023, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5) : 735-756.
 PDF(36153 KB)
PDF(36153 KB)
 PDF(36153 KB)
PDF(36153 KB)
Stimuli-Responsive Polymer Microneedle System for Transdermal Drug Delivery
Compared with oral administration and injection administration, the microneedle transdermal delivery system has the characteristics of high efficiency, safety and painless administration. In particular, the stimuli-responsive polymer microneedle systems exhibit good biocompatibility and can be realized according to the micro-changes in the environment. The function of percutaneous local and systemic intelligent drug delivery in time and space is currently an international frontier research topic. This paper focuses on the research of stimulus-responsive polymer microneedles at home and abroad in the past ten years, and focuses on the evolution of polymer microneedles, the types of internal and external environmental stimulus response and its response structure-activity mechanism. In addition, the preparation and characterization of microneedles and the application of microneedle system in the fields of biomedicine delivery, tissue and organs, dermatology and medical beauty are described in detail. The stimulation-responsive polymer microneedle system has the advantages of simple use, adjustable mechanical properties and precise targeted drug delivery, which has great research significance in the field of percutaneous targeted drug delivery. In the future, the biological in vivo load and industrial application of standardization are the direction of continuous efforts and progress of researchers.
1 Introduction
2 Preparation process and characterization methods of stimuli-responsive polymer microneedles
2.1 Preparation
2.2 Methods for characterizing the properties of polymer microneedle systems
3 Classification of stimulus-responsive polymer microneedles
3.1 Polymer microneedle system triggered by external environmental stimuli
3.2 Polymer microneedle system triggered by in vivo physiological signal stimuli
4 Stimuli-responsive polymer microneedles for transdermal delivery
4.1 Biopharmaceutical delivery
4.2 Tissue organ therapy
4.3 Detection and sensing device
4.4 Extraction of samples
4.5 Dermatology and cosmetics
5 Conclusion and outlook
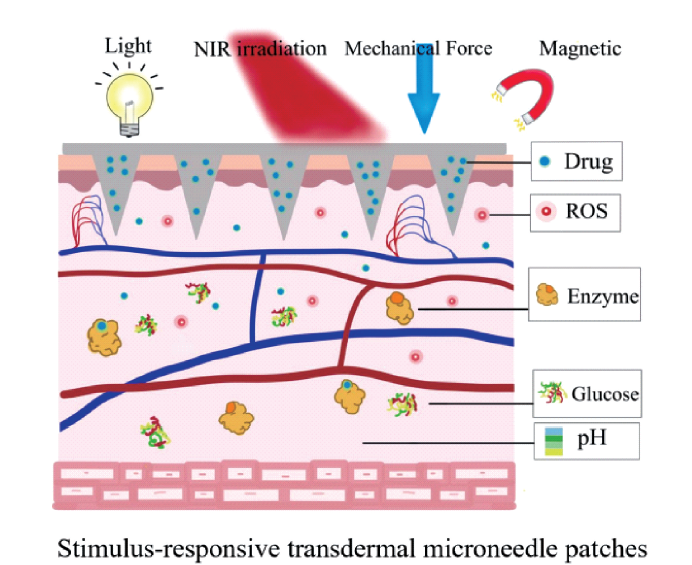
polymer microneedles / stimulus responsiveness / transdermal drug delivery / disease treatment
| [1] |
(陈明龙, 杨丹, 孙颖, 权桂兰, 吴传斌, 潘昕. 药学进展, 2020, 44(5): 324. ).
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
(陈永杭, 李欣芳, 余伟江, 王幽香. 化学进展, 2021, 33(07): 1152).
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
Ullah, Khan, Choi, Kim. Polymers, 2019, 11(11): 1834.
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
(陈怡, 宋婷, 陈雯琳, 李海梁, 卢爱玉, 张峻颖. 药学研究, 2021, 40(11): 744.).
|
| [12] |
(张朵朵, 吴艳丽, 鞠大宏, 刘梅洁, 郝保华. 中华中医药杂志, 2014, 29(8): 2559.).
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
(赵笑, 李欣芳, 张鹏, 王幽香. 化学进展, 2017, 29(12): 1518.).
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
(杨倩丽, 康晓明, 孙静, 魏柳荷, 马志. 化工进展, 2015, 34(08): 3075).
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
(蔡紫煊, 张斌, 姜丽阳, 许国贺, 马晶军. 化学进展, 2019, 31(12): 1653.).
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |