 PDF(2856 KB)
PDF(2856 KB)


Performance of Resistance to Sulfur Oxide and Regeneration over Copper-Based Small-Pore Zeolites Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3
Shuai Li, Na Zhu, Yangjian Cheng, Di Chen
Prog Chem ›› 2023, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5) : 771-779.
 PDF(2856 KB)
PDF(2856 KB)
 PDF(2856 KB)
PDF(2856 KB)
Performance of Resistance to Sulfur Oxide and Regeneration over Copper-Based Small-Pore Zeolites Catalysts for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3
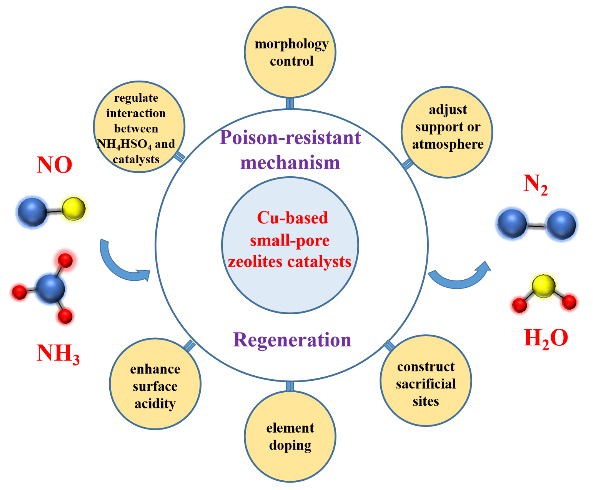
Copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts are the promising candidate catalysts for NOx abatement in current diesel vehicles with Chinese VI standards, due to the excellent NH3-SCR catalytic performance, hydrothermal stability, nitrogen selectivity and wide temperature window. However, the catalytic activity of copper-based small-pore zeolites is still significantly affected by sulfur oxides emitted from diesel vehicles, and even the irreversible deactivation occurs. The SO2-poisoning of Cu-based small-zeolites is mainly due to the accumulation of surface ammonium sulfate and sulfation of Cu active site sites. In this review, the research status of the structure and active sites of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts is summarized, and the sulfur poisoning mechanism of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts is discussed. Moreover, the research advance in the improvement of sulfur resistance of catalysts and the regeneration of sulfur-poisoned catalysts is also illustrated. The systematic understanding of mechanism of sulfur poisoning and regeneration is important for the design of novel, efficient catalyst. It is pointed out that the study on sulfur poisoning mechanism and regeneration mechanism of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts, as well as the synergistic effect of various poisoning factors and corresponding deactivation mechanism, are the main research directions for copper-based zeolites to be practically applied to ultra-low emission of nitrogen oxides in diesel vehicle exhaust in the future.
1 Introduction
2 Structure and active sites of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts
2.1 Structure of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts
2.2 Study on active sites of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts
3 Study on sulfur poisoning mechanism of copper-based small-pore zeolites catalysts
3.1 The effect of SO2
3.2 The effect of H2O and SO2coexistence
3.3 The effect of SO3
4 Research advance on improvement of resistance to sulfur oxides
4.1 Element doping
4.2 Morphology control
5 Regeneration research
5.1 Study of regeneration methods
5.2 Research on regeneration mechanism
6 Conclusion and outlook
nitrogen oxides / copper-based small-pore zeolites / selective catalytic reduction / sulfur poisoning / regeneration
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
2021年中国移动源环境管理年报. 中华人民共和国生态环境部, 2021.
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |