 PDF(26096 KB)
PDF(26096 KB)


High Voltage Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries
Qimeng Ren, Qinglei Wang, Yinwen Li, Xuesheng Song, Xuehui Shangguan, Faqiang Li
Prog Chem ›› 2023, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (7) : 1077-1096.
 PDF(26096 KB)
PDF(26096 KB)
 PDF(26096 KB)
PDF(26096 KB)
High Voltage Electrolytes for Lithium Batteries
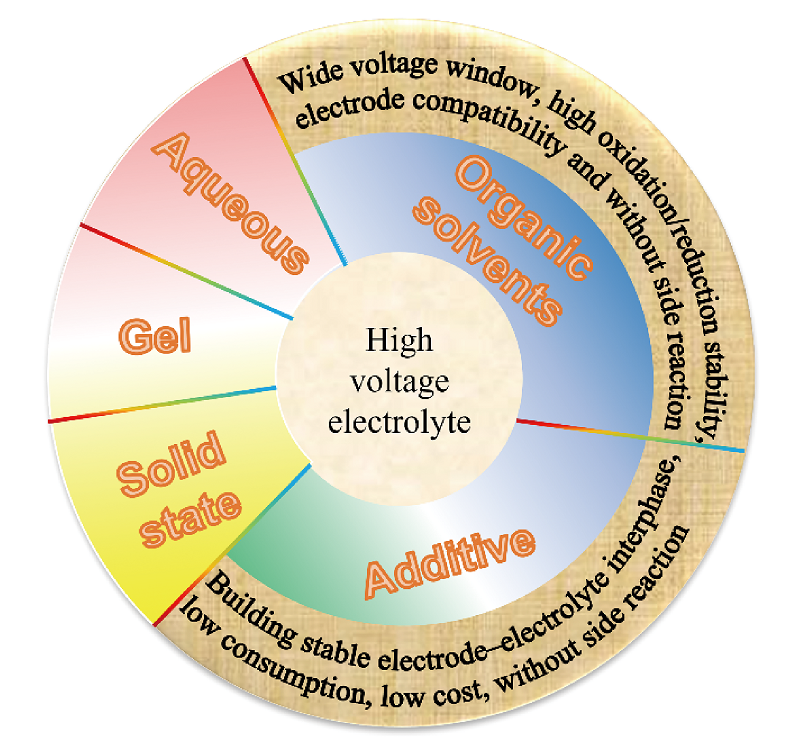
With the proposal of "peak carbon dioxide emissions" and "carbon neutral" strategic objectives, developing clean energy and promoting the development of new energy industry has become the consensus of the whole society. Lithium battery as the candidate for new generation of energy storage equipment due to its remarkable advantages such as high energy density, high power density, long cycle life and environmental friendliness. Its development plays a significant role in alleviating energy crisis, driving the conversion of old kinetic energy into new and achieving the strategic goal of "carbon peaking and carbon neutrality". In order to further improve the energy density of lithium batteries, the most effective strategy is to use high voltage or high specific capacity cathode materials. However, due to the low oxidation stability and narrow electrochemical window of traditional carbonate ester electrolytes, they are prone to oxidative decomposition when the working voltage exceeds 4.2 V, which cannot be cycled stably at high voltages, so it is particularly important to broaden the electrochemical window of electrolytes. This paper mainly discusses the mechanism of organic solvents and additives in high-voltage electrolytes, explores effective methods to broaden the electrochemical window of new electrolytes, summarizes the characteristics of aqueous electrolytes, solid electrolytes, and polymer gel electrolytes, and finally; summarizes and outlooks the future development and prospects of high-voltage electrolytes to provide scientific basis for the design and development of high-voltage electrolytes for lithium batteries.
1 Introduction
2 Working mechanism of high voltage electrolyte
3 Research progress on the high-voltage electrolyte for lithium batteries
3.1 New electrolyte organic solvents
3.2 High voltage electrolyte additive
3.3 Aqueous electrolyte
3.4 Solid state electrolyte
3.5 Gel polymer electrolyte
4 Conclusion and outlook
lithium battery / high voltage / electrochemistry / electrolytes / solvents / additive
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [154] |
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
|
| [157] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |