 PDF(8159 KB)
PDF(8159 KB)


Micro-/Nanorobots for Enhanced Antibacterial Treatment
Ting Liu, Shiyao Pang, Xiaohui Yan
Prog Chem ›› 2023, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (7) : 997-1004.
 PDF(8159 KB)
PDF(8159 KB)
 PDF(8159 KB)
PDF(8159 KB)
Micro-/Nanorobots for Enhanced Antibacterial Treatment
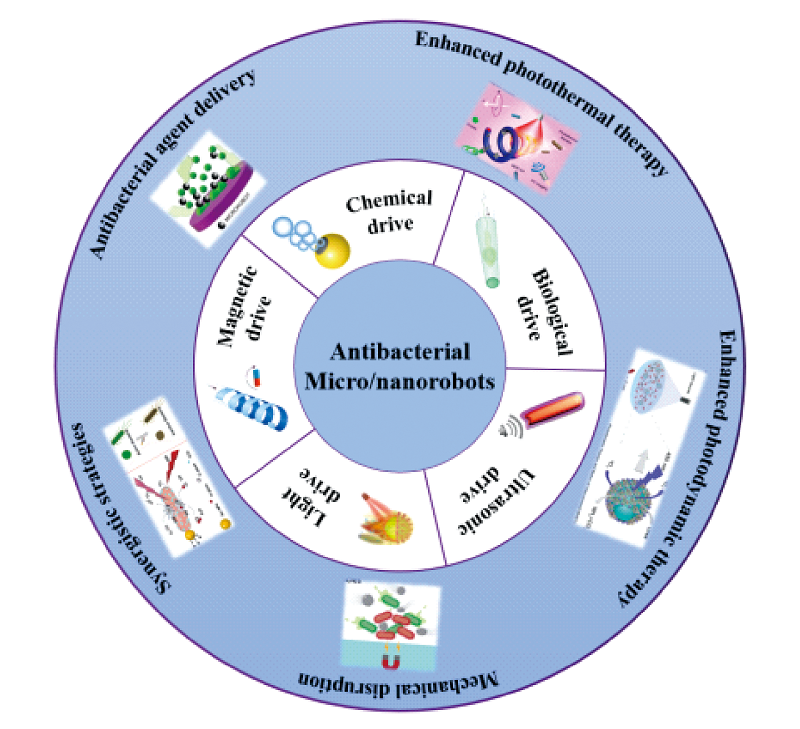
Bacterial infections, becoming the second leading cause of death in the worldwide, pose a serious threat to public health. Plenty of therapeutic strategies, such as antibiotic therapy, photothermal therapy, photodynamic therapy and sonodynamic therapy, etc., have been developed to treat bacterial infections. However, how to improve the efficiency of antibacterial therapy is still a great challenge. Micro-/nanorobots, as miniaturized robots with active motion properties, are promising to provide new therapeutic strategies for effective antibacterial. On the one hand, micro-/nanorobots can accurately deliver antibacterial media to the micro area of the lesion through their controllable directional movement. On the other hand, the motion of swarms of micro-/nanorobots can also cause mechanical effect and fluid stirring effects, which mechanically damage the pathogen and at the same time, promote the full reaction between pathogens and antibacterial media, so as to enhance the antibacterial efficiency synergistically. In this review, we summarize the important research advances of micro-/nanorobots in the field of antibacterial applications, and start from the driving mode of antibacterial micro-/nanorobots, systematically expounding the mechanism of action and application advantages in various antibacterial treatments. Finally, we discuss the potential challenges faced by micro-/nanorobots in antibacterial therapy and prospect the main directions of future research in this field.
1 Introduction
2 Driving mode of antibacterial micro-/nanorobots
3 Micro-/nanorobots in antibacterial application
3.1 Antibacterial agent delivery
3.2 Enhanced photothermal therapy
3.3 Enhanced photodynamic therapy
3.4 Mechanical disruption
3.5 Synergistic strategies
4 Conclusion and outlook
micro-/nanorobots / synergy effect / precise control / antibacterial treatment / active delivery
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |