 PDF(85792 KB)
PDF(85792 KB)


Research Progress of Ni-Rich Cathode Materials
Tianyu Wang, Li Wang, Wei Sun, Meirong Wu, Yue Yang
Prog Chem ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (7) : 1026-1045.
 PDF(85792 KB)
PDF(85792 KB)
 PDF(85792 KB)
PDF(85792 KB)
Research Progress of Ni-Rich Cathode Materials
Benefiting from high energy density and low cost,Ni-rich LiNixCoyMn/Al1-x-yO2materials have received great attention as promising cathode candidates for next-generation high-energy lithium-ion batteries(LIBs)that are widely used in electric vehicles(EVs).However,with an increased Ni content,Ni-rich cathode materials suffer from severe structural,chemical,and mechanical instabilities,seriously restricting their industrially safe application in power LIBs of EVs.In this review,primarily,the synthesis methods of Ni-rich cathode materials are summarized in detail,which include solid-state method,sol-gel method,hydrothermal method,spray-drying method,and co-precipitation method.Subsequently,the key failure mechanisms,including ion mixing and irreversible phase transition,residual Li species and interface side reactions,mechanical microcracks,and transition metal dissolutions,are thoroughly analyzed throughout the preparation,storage,and service of Ni-rich cathode materials,thereby clarifying various performance decay behaviors of materials.The modification strategies that cover ion doping,surface coating,core-shell/gradient materials,and single-crystal materials are systematically discussed for Ni-rich cathode materials,aiming at presenting conspicuous research progress and current shortcomings for the stabilization of Ni-rich cathode materials.Finally,this review presents a perspective toward future development and optimization for Ni-rich cathode materials,aiming at delivering a theoretical guidance for propelling its industrial safe application in high-energy LIBs 。
1 Introduction
2 Synthetic method
2.1 Solid-state method
2.2 Sol-gel method
2.3 Hydrothermal method
2.4 Spray-drying method
2.5 Coprecipitation method
3 Failure mechanism
3.1 Ion mixing and irreversible phase transition
3.2 Surface residual Li species and interface side reaction
3.3 Microcracks induced by internal stress
3.4 Dissolution of transition metals
4 Modification method
4.1 Ion doping
4.2 Surface coating
4.3 Core-shell/gradient material design
4.4 Single-crystal material design
5 Conclusion and outlook
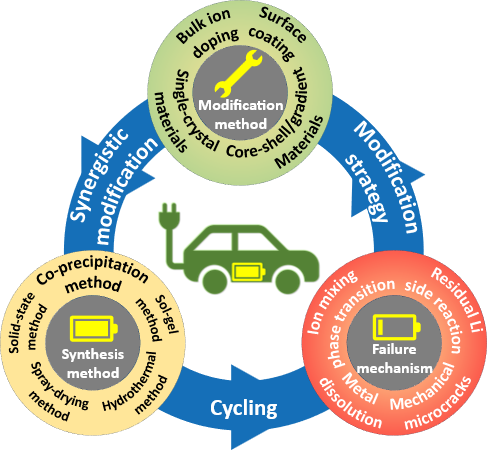
Ni-rich cathode materials / synthesis methods / failure mechanism / modification methods / synergistic modification
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
(杨续来, 袁帅帅, 杨文静, 刘闯, 杨世春. 机械工程学报, 2023, 59: 239.).
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |