 PDF(146208 KB)
PDF(146208 KB)


Preparation of GroupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2 Quantum Dots and Light-Emitting Diode Devices
Fanghai Liu, Hui Jiang, Shuqi Yang, Qi Liu, Lei Chen
Prog Chem ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (7) : 1046-1060.
 PDF(146208 KB)
PDF(146208 KB)
 PDF(146208 KB)
PDF(146208 KB)
Preparation of GroupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2 Quantum Dots and Light-Emitting Diode Devices
Quantum dots are considered as ideal luminescent materials for high color gamut,flexible,and large area display,medical devices,and the application of other fields,due to their unique photoelectric properties.Compared with the quantum dots of binaryⅡ-ⅥorⅢ-Ⅴgroup,the quantum dots of ternaryⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2group have significant advantages in terms of ecological and environmental friendliness without containing Cd or Pb elements,large Stokes shift with adjustable band gap,long-life luminescence,etc.Moreover,it is facile to obtain emission wavelength adjustable continuously from visible to near-infrared region by changing chemical elements ratio in the composition of singleⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2family.These characters make theⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2quantum dots have broad application prospects in the fields of light-emitting diodes,solar cells,photodetectors,biological imaging,etc.This paper systematically reviews the synthesis methods and optical performance optimization strategies of quantum dots and those suitable for I-III-VI2quantum dots,explains the luminescence mechanisms of I-III-VI2quantum dots based on their electronic band structures,summarizes recent-years progress of quantum dots application in lighting and display devices,and focuses on the application progress of the I-III-VI2quantum dots in photo-and electroluminescent diodes.Finally,the future prospects and challenges of I-III-VI2quantum dots are prospected 。
1 Introduction
2 Quantum dot synthesis method
2.1 Top-down synthesis
2.2 Bottom-up-heat injection method
2.3 Bottom-up-one-pot hot method
3 Current status of research based on groupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2quantum dots
3.1 Luminescence mechanisms of groupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2quantum dots
3.2 Optimization of optical properties of groupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2quantum dots
4 GroupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2quantum dot light emitting devices
4.1 Quantum dot luminescent display
4.2 GroupⅠ-Ⅲ-Ⅵ2quantum dot QLED and WLED devices
5 Conclusion and outlook
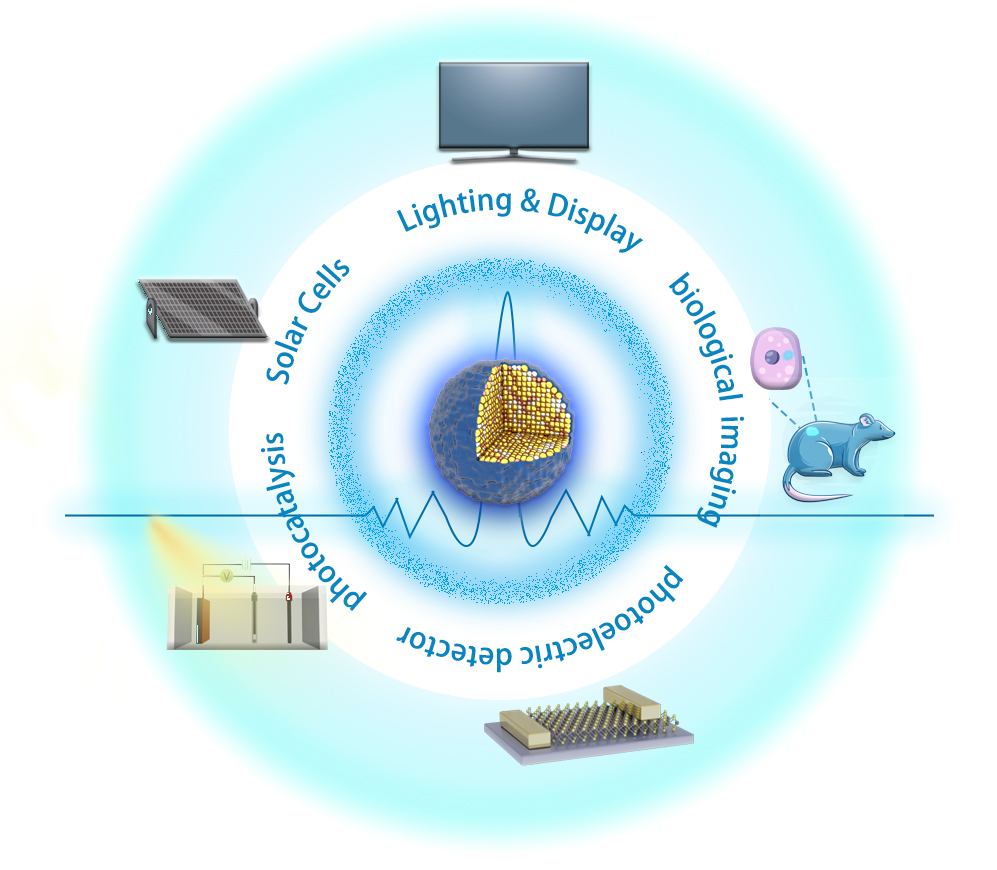
quantum dot synthesis methods / luminescence mechanism / optical performance optimization / QLED / WLED
| [1] |
García de Arquer F P,
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |