 PDF(20549 KB)
PDF(20549 KB)


Synthesis and Cancer Biomedical Applications of Dendrimer-Based Fluorescence Imaging Agents
Linjie Yue, Lingxiu He, Na Liu, Risong Pan, Jingyi Zhu
Prog Chem ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8) : 1186-1199.
 PDF(20549 KB)
PDF(20549 KB)
 PDF(20549 KB)
PDF(20549 KB)
Synthesis and Cancer Biomedical Applications of Dendrimer-Based Fluorescence Imaging Agents
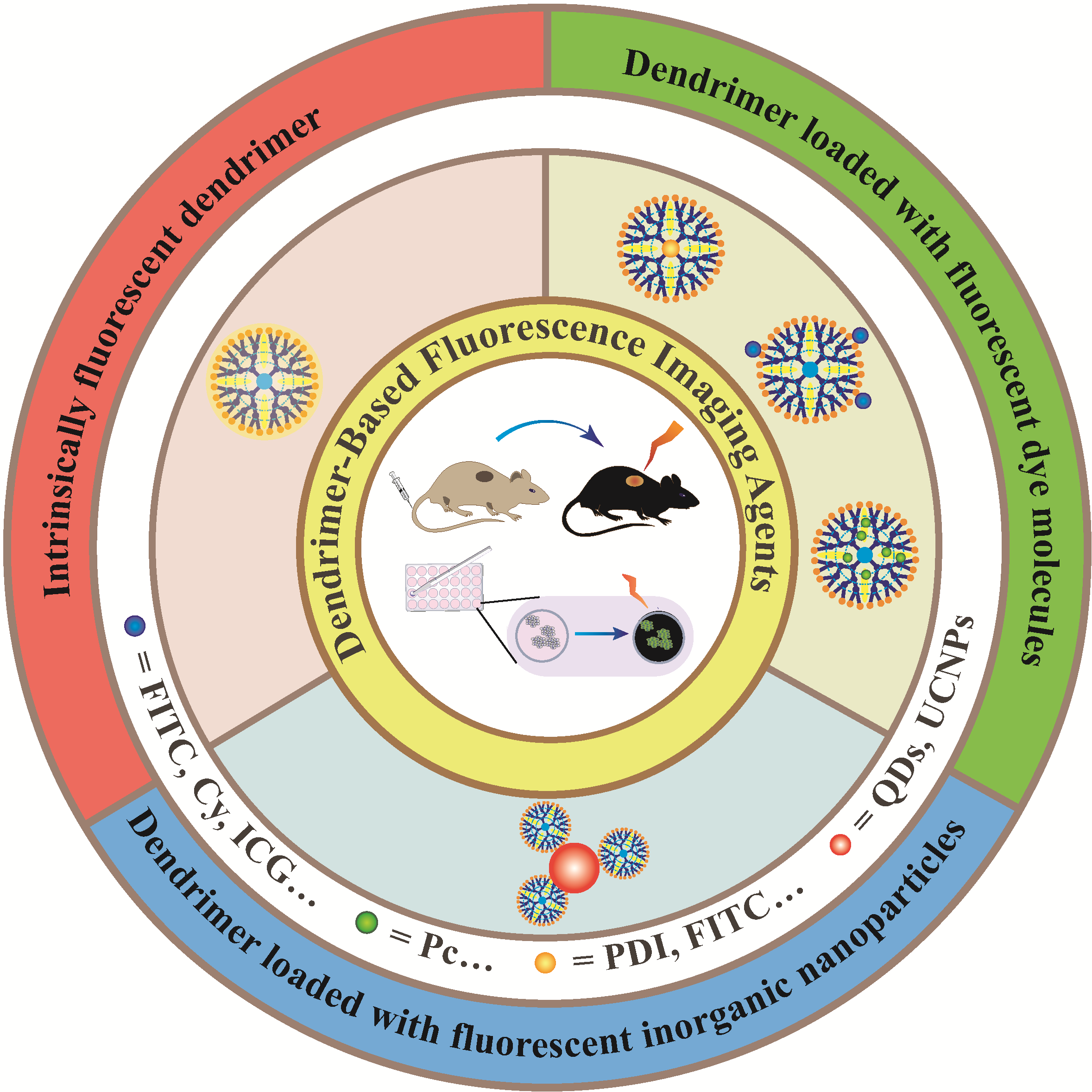
as a molecular imaging technique with high sensitivity and high spatial resolution,fluorescence imaging is widely used in cancer diagnosis and therapy.However,commonly used fluorescence imaging agents,such as small-molecule fluorescent dyes and fluorescent inorganic nanoparticles,have defects such as poor photostability,rapid metabolism in vivo,and low accumulation at lesion sites,which limit their application in the field of cancer fluorescence imaging.in recent years,the appearance of dendrimer has provided a new strategy for the development of nano-scale fluorescence imaging agents.A dendrimer is composed of three parts,including a central core,internal repeating units and abundant terminal functional groups.the excellent structure of dendrimer enables it to load small-molecule fluorescent dyes or fluorescent inorganic nanoparticles to achieve early fluorescence monitoring of cancer and evaluate its distribution and metabolism in vivo.Additionally,some amino-terminated dendrimers can be used to monitor their uptake by cancer cells through their intrinsic fluorescence.the introduction of dendrimer greatly improves the water solubility and biocompatibility of fluorescent dyes and fluorescent inorganic nanoparticles,and the surface functionalization of dendrimer could achieve their tissue-specific delivery.Most importantly,the protection of dendrimer can greatly avoid fluorescence quenching and achieve long-time fluorescence imaging.Therefore,this review mainly describes various kinds of dendrimer-based fluorescence imaging agents,summarizes their synthesis methods and their applications in cancer fluorescence imaging,and prospects for their future development。
Contents
1 Introduction
2 Functionalized dendrimer with fluorescence property
2.1 Intrinsically fluorescent dendrimer
2.2 Dendrimer loaded with fluorescent dye molecules
2.3 Dendrimer loaded with fluorescent inorganic nanoparticles
3 Conclusion and outlook
molecular imaging / dendrimer / fluorescence imaging / nanocarrier / biomedical application
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |