 PDF(9144 KB)
PDF(9144 KB)


Stimulus-Responsive Multifunctional Nucleic Acid Hydrogels Based on Cell Capture and Release
Danyu Wang, Mengke Guo, Zihan Guo, Mengyu Huang, Hua Yi, Kaixiang Zhang
Prog Chem ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (10) : 1567-1580.
 PDF(9144 KB)
PDF(9144 KB)
 PDF(9144 KB)
PDF(9144 KB)
Stimulus-Responsive Multifunctional Nucleic Acid Hydrogels Based on Cell Capture and Release
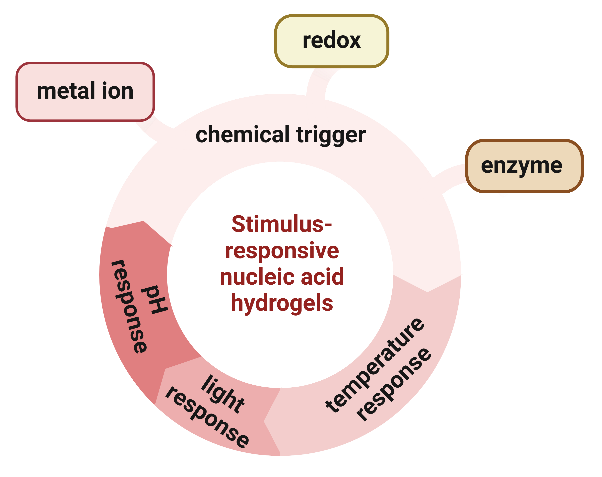
Nucleic acid hydrogels have good hydrophilicity, adjustability and biocompatibility, which have attracted considerable attention in the past few years, especially in the field of biomedicine and smart materials. Nucleic acid hydrogel is stimulus-responsive, meaning that external stimuli such as pH changes, light, temperature variations, and chemical triggers (including metal ion response, redox response, and enzyme response) can induce physical and chemical changes within them. Consequently, they are capable of perceiving their environment and undergoing responsive deformation, enabling precise cell therapy that can be controlled both temporally and spatially. Cell capture and release using stimulus-responsive nucleic acid hydrogels can control and modulate cellular behavior, and can also play an important role in biomedical research and applications, such as targeted drug therapies using the capture and release of specific cell types. Based on this, this paper summarizes the preparation methods of pure nucleic acid hydrogels and polymer-nucleic acid hybrid hydrogels, further discusses the application strategies of different stimuli-responsive nucleic acid hydrogels, and focuses on the research progress of cell capture and release in cell imaging, cell therapy and synergistic drug delivery. Finally, we discuss the urgent problems that need to be addressed in the research of nucleic acid hydrogels, and provide a prospect for their future development.
Contents
1 Introduction
2 Preparation of nucleic acid hydrogels
2.1 Pure nucleic acid hydrogel
2.2 Polymer-nucleic acid hybrid hydrogel
3 Stimulus-responsive nucleic acid hydrogels
3.1 pH response
3.2 Light response
3.3 Temperature response
3.4 Chemical trigger
4 Stimulus-responsive nucleic acid hydrogels used for cell capture and release
4.1 Cell imaging
4.2 Cell therapy
4.3 Collaborative drug delivery
5 Conclusion and outlook
nucleic acid hydrogels / stimulus-responsive / cell capture / cell release / biomedicine
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
(马翾, 张洋子, 许文涛. 生物技术进展, 2019, 9(6): 554.)
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
(杨勃, 孙立梅, 潘玙璠, 董原辰, 孙亚伟, 刘冬生. 高分子学报, 2021, 52 (8):996.)
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
(程平, 张洋子, 马翾, 陈旭, 朱保庆, 许文涛. 中国生物工程杂志, 2020, 40 (3):132. )
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
(潘国莹, 张吉傲笛, 梁永平, 郭保林. 四川大学学报(医学版), 2023, 54 (4):726.)
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |