 PDF(8373 KB)
PDF(8373 KB)


Principle and Application of Algae Concentration Prediction Models in Lakes and Reservoirs
Yuxuan Xie, Jun Wang, Yuqing Tang, Yun Zhu, Zehui Tian, Alex T. Chow, Chao Chen
Prog Chem ›› 2024, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9) : 1412-1424.
 PDF(8373 KB)
PDF(8373 KB)
 PDF(8373 KB)
PDF(8373 KB)
Principle and Application of Algae Concentration Prediction Models in Lakes and Reservoirs
the risk of algal blooms has significantly increased in eutrophic lakes and reservoirs due To the global climate change and anthropogenic pollution,which has a significant impact on the safety and stability of municipal water supplies.to protect source water,it is necessary to construct a mathematical model and alert system to predict algae concentration in lakes and reservoirs.This paper reviews the main environmental factors(physical,chemical,and biological)that affect the algae growth,and summarizes the principles and application scenarios of existing models.Prediction models can generally be divided into two categories:process-based models(PB models)and data-driven models(DD models).PB models are based on natural processes,which enhances their interpretability and generality.However,they require a high level of research and testing,which can be costly.DD models rely on artificial intelligence methods such as machine learning,which offer flexible and diverse modeling approaches.However,they depend on data quality,lack mechanism support,and are location-specific.Both models have been extensively studied in the past decades and have been applied in some lakes and reservoirs.to further improve model performance,future research should improve the frequency and quality of data monitoring and combine natural process mechanisms with artificial intelligence methods。
1 Introduction
1.1 Eutrophication
1.2 Impacts of algal blooms
2 Influencing Factors
2.1 Physical factors
2.2 Chemical factors
2.3 Biological factors
3 Algae concentration prediction model
3.1 Process-based models
3.2 Data-driven models
3.3 Pro and cons
4 Conclusion and suggestions
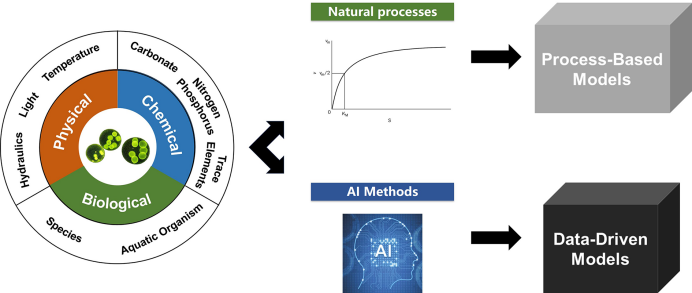
lakes and reservoirs / algal blooms / influencing factors / algae concentration prediction / process-based models / data-driven models
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
(张悦. 城市供水系统应急净水技术指导手册. 第2版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2017.).
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
(刘雪梅, 章光新. 水科学进展, 2022, 33(02): 316.)
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
(龚川, 贡丹丹, 刘德富, 张佳磊, 严广寒. 环境科学研究, 2020, 33(05): 1214.).
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
(秦伯强, 王小冬, 汤祥明, 冯胜, 张运林. 地球科学进展, 2007, 22(9): 896.).
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
(梁培瑜, 王烜, 马芳冰. 湖泊科学, 2013, 25(04): 455.).
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
(孔繁翔, 马荣华, 高俊峰, 吴晓东. 湖泊科学, 2009, 21(3): 314.).
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
(许秋瑾, 秦伯强, 陈伟民, 陈宇炜, 高光. 湖泊科学, 2001, (02): 149.).
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
(陈宇炜, 秦伯强, 高锡云. 湖泊科学, 2001, (01): 63.).
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
(王小艺, 赵载平, 刘载文, 许继平, 董硕琦. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(07): 1677.).
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |