 PDF(20933 KB)
PDF(20933 KB)


Progress in the Applications of Polymer-Decorated Black Phosphorus and Black Phosphorus Analog Nanomaterials in Biomedicine
Aoqi Su, Xinyu Li, Ran Wang, Lili Gao, Tifeng Jiao
Prog Chem ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2) : 133-156.
 PDF(20933 KB)
PDF(20933 KB)
 PDF(20933 KB)
PDF(20933 KB)
Progress in the Applications of Polymer-Decorated Black Phosphorus and Black Phosphorus Analog Nanomaterials in Biomedicine
In the realm of two-dimensional nanomaterials, black phosphorus (BP) is considered a promising candidate to address the shortcomings of graphene and transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs). Low- dimensional black phosphorus (BP) refers to a class of nanomaterials derived from the layered semiconductor BP. These materials exhibit high structural anisotropy, tunable bandgap widths, and high hole and electron mobility, endowing BP with unique properties such as conductivity, photothermal, photodynamic, and mechanical behaviors. BP's near-infrared light response significantly enhances its effectiveness in photothermal and photodynamic antibacterial applications. Additionally, due to its unique layered structure, BP nanosheets (BPNS) possess a high surface-to-volume ratio, making them excellent carriers for loading and delivering other antimicrobial nanomaterials or drugs. First, this article discusses the physical properties of low-dimensional BP and introduces various preparation methods. Furthermore, it systematically reviews exciting therapeutic applications of polymer-modified black phosphorus nanomaterials in various fields, such as cancer treatment (phototherapy, drug delivery, and synergistic immunotherapy), bone regeneration, and neurogenesis. Finally, the paper discusses some challenges facing future clinical trials and potential directions for further research.
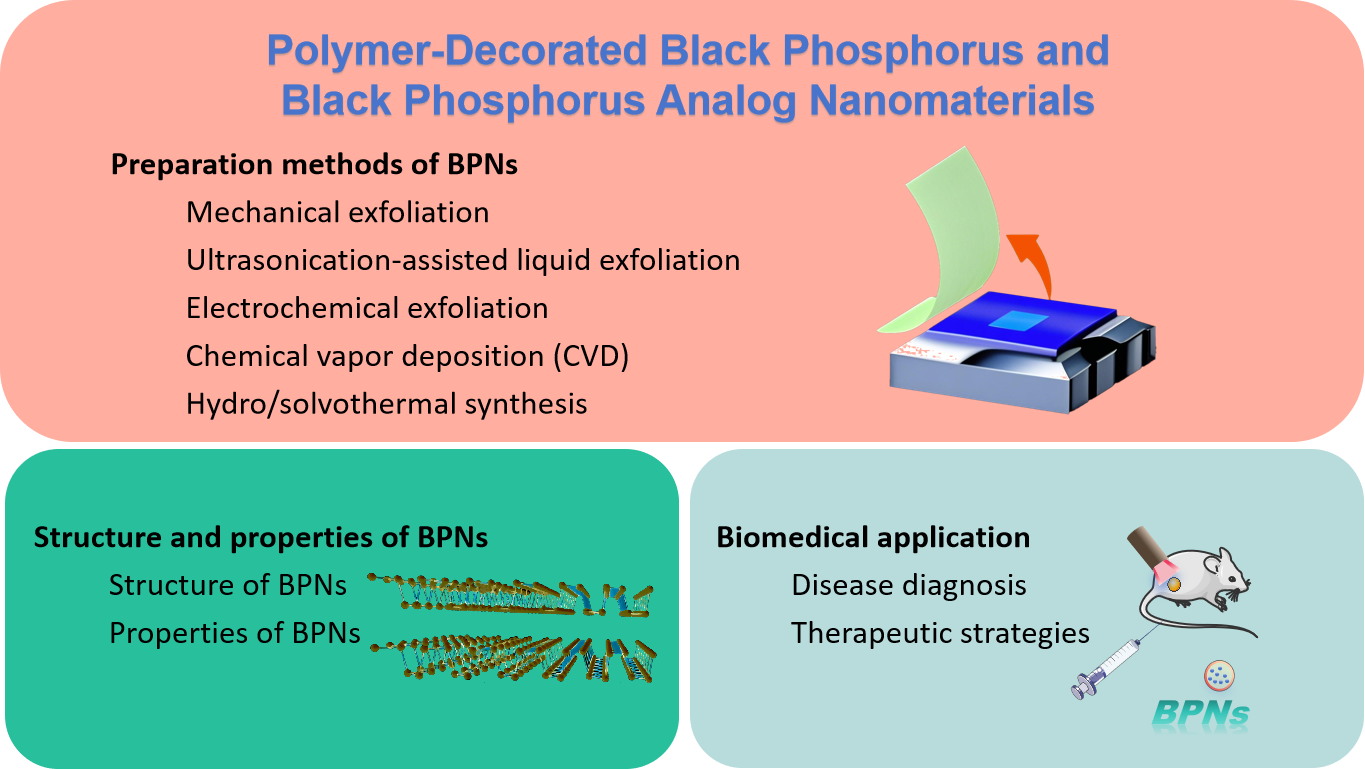
1 Introduction
2 Preparation methods of BPNs
2.1 Mechanical exfoliation
2.2 Ultrasonication-assisted liquid exfoliation
2.3 Electrochemical exfoliation
2.4 Chemical vapor deposition (CVD)
2.5 Hydro/solvothermal synthesis
3 Structure and properties of BPNs
3.1 Structure of BPNs
3.2 Properties of BPNs
4 Biomedical application
4.1 Disease diagnosis
4.2 Therapeutic strategies
5 Conclusion and outlook
low-dimensional black phosphorus / bioimaging / physical properties / biomedical applications
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [154] |
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |