 PDF(1663 KB)
PDF(1663 KB)


The Impact of Aging on the Physicochemical Properties, Environmental Processes and Toxic Effects of Microplastics
Yulong Wang, Yue Li, Fengbang Wang, Maoyong Song
Prog Chem ›› 2025, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1) : 46-58.
 PDF(1663 KB)
PDF(1663 KB)
 PDF(1663 KB)
PDF(1663 KB)
The Impact of Aging on the Physicochemical Properties, Environmental Processes and Toxic Effects of Microplastics
Microplastic pollution has become a major environmental issue of global concern. Microplastics can undergo aging under various environmental conditions. The aging process will change the physical and chemical properties of microplastics, thereby leading to changes in their environmental behaviors and toxicities. Therefore, exploring the aging process and mechanism of microplastics is of significance for understanding the environmental processes and health risks of microplastics. This article focuses on the aging process of microplastics in the environment and reviews it from the aspects of aging pathways, influencing factors, interactions with pollutants, release of chemical substances, and changes in toxicities. It also looks forward to the existing challenges and future research directions in the current studies on microplastic aging.
1 Introduction
2 Pathways of microplastics aging
2.1 Physical aging of microplastics
2.2 Chemical aging of microplastics
2.3 Biological aging of microplastics
2.4 Artificial aging of microplastics
3 The factors influencing microplastics aging
3.1 The impact of physical and chemical properties on microplastics aging
3.2 The impact of environmental conditions on microplastics aging
4 The impact of aging on microplastics
4.1 The impact of aging on the physical and chemical properties of microplastics
4.2 The impact of aging on the interaction between microplastics and pollutants
4.3 The impact of aging on the release of chemicals from microplastics
4.4 The impact of aging on the toxicities of microplastics
5 Conclusions and perspectives
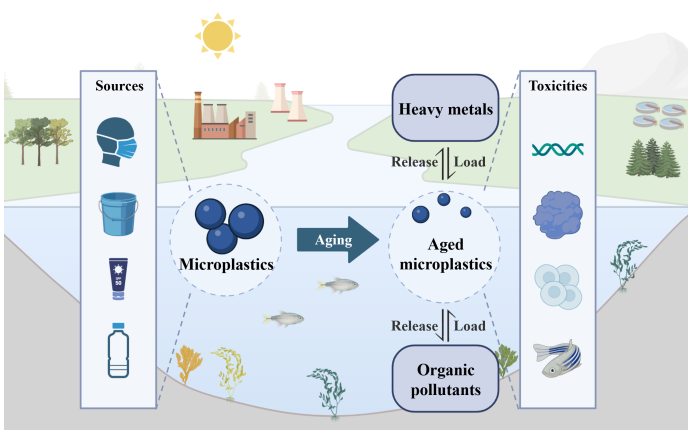
microplastics / aging / influencing factors / pollutants loading / additives leaching / toxic effects
| [1] |
Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Global Plastics Outlook: Policy Scenarios to 2060, OECD Publishing, Paris, 2022.
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
Campanale, Massarelli, Savino, Locaputo, Uricchio. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health, 2020, 17: 1212.
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [154] |
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
|
| [157] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |