

Piezoelectric Biosensor and Its Application in Healthcare
Received date: 2023-12-14
Revised date: 2024-04-09
Online published: 2024-07-01
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22004009)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(U2006218)
Beijing Natural Science Foundation(2214057)
R&D Program of Beijing Municipal Education Commission(KM202111232005)
Project of Construction and Support for high-level Innovative Teams of Beijing Municipal Institutions(BPHR20220124)
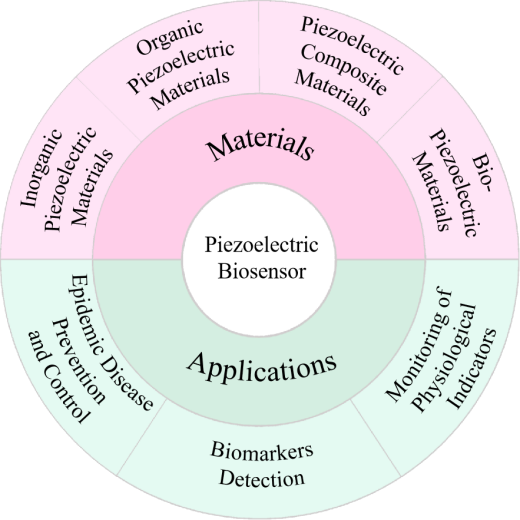
With the rapid development of social economy and the continuous improvement of people's living standards,medical and health care have taken on an important strategic position.as an important analytical detection method,biosensing technology plays a key role in the field of medical health.piezoelectric biosensor,as a new kind of biosensor,utilizes piezoelectric materials for biological analysis.piezoelectric biosensor has the advantages of good stability,fast detection speed,high accuracy and simple operation,and has important application value in biomedicine,health monitoring and disease prevention and control.Herein,we review the research progress of piezoelectric biosensor home and abroad in recent years,and introduce the principle of piezoelectric biosensors based on the piezoelectric effect of quartz crystal microbalance and the commonly used piezoelectric materials,including inorganic piezoelectric materials,organic piezoelectric materials,piezoelectric composite materials and biological piezoelectric materials.in addition,the applications of piezoelectric biosensors in human health monitoring and disease prevention and control are also introduced,such as the monitoring of physiological signs,such as heart rate,blood pressure and pulse,the detection of biomarkers and epidemic viruses such as SARS-CoV-2(COVID-19).Finally,the current problems faced by piezoelectric biosensors are summarized,and the future development of piezoelectric biosensors is prospected。
1 Introduction
2 Working principle
3 Piezoelectric materials
3.1 Inorganic piezoelectric materials
3.2 Organic piezoelectric materials
3.3 Piezoelectric composite materials
3.4 Bio-piezoelectric materials
4 Applications in healthcare
4.1 Monitoring of physiological indicators
4.2 Biomarkers detection
4.3 Epidemic disease prevention and control
5 Conclusion and outlook
Xingping Zhong , Yanxia Chen , Chen Chen , Lei Qin , Xueji Zhang . Piezoelectric Biosensor and Its Application in Healthcare[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2024 , 36(7) : 975 -986 . DOI: 10.7536/PC231203
表1 Types and Applications of Piezoelectric MaterialsTable 1 Summary of types and applications of piezoelectric materials。 |
| Type | Materials | Applications | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inorganic | Quartz crystal | Bilirubin, Bacteria, Uric acid | 34,36,37 |
| PZT | Self-powered, Joint, Virus | 40,41,42 | |
| Zinc oxide | Swimming, Fingerprint | 46,47 | |
| Aluminium nitride | Escherichia coli, Sweat | 49,50 | |
| Barium titanate | Glucose | 51 | |
| Organic | Polyvinylidene fluoride | Microdeformation, Body signs, bacteriostatic | 53,54,56 |
| Polyhydroxybutyrate | Bio-scaffolds | 57 | |
| Polyvinylidene-fluoride-trifluoroethylene | Bacteriostatic | 57 | |
| Composite | Piezoelectric 1-3 composite material | Blood pressure | 60 |
| Glycine - chitosan composite material | Biomedical | 61 | |
| Gold modified barium titanate | Bacteriostatic | 62 | |
| Biologic | Diphenylalanine film | Biosensing | 65 |
| γ -glycine crystal | Biosensing | 66 | |
| Across a membrane proteincrystal | Tissue regeneration | 67 | |
| DNA membrane | Biological | 69 |
图2 无机压电材料:(a)PZT薄膜[40] ;(b)PZT薄膜压电生物传感器[41] ;(c)ZnO纳米线自供电生物传感器[46]Fig. 2 Inorganic piezoelectric materials:(a)PZT thin film [40]. Copyright 2014, Advanced Materials(b)PZT thin film piezoelectric biosensor[41]. Copyright 2022, IEEE(c)Synthesis of self-powered biosensors based on ZnO nanowires [46]. Copyright 2021, Biosensors |
图3 有机压电材料:(a)基于有机压电材料PVDF的压电传感器[53];(b)PVDF链与肽键结合[54];(c)聚羟基丁酸脂压电材料[57];(d)压电纳米纤维[58]Fig. 3 Organic piezoelectric materials:(a)piezoelectric sensor based on organic piezoelectric material PVDF [53], Copyright 2020, Elsevier; (b)binding of PVDF chain to peptide bond [54], Copyright 2022, Elsevier; (c)polyhydroxybutyrate piezoelectric material [57], Copyright 2020, Polymers;(d)piezoelectric nanofibers [58], Copyright 2020, Elsevier |
图4 压电复合材料:(a)1-3型压电复合材料[60] ;(b)甘氨酸/壳聚糖(glycine/chitosan,Gly/CS)膜压电复合材料[61] ;(c)金纳米粒子修饰钛酸钡纳米立方体(Au@BTO)压电复合材料[62]Fig. 4 Piezoelectric composite materials:(a)1-3 composite piezoelectric materials [60]. Copyright 2020, IEEE; (b)Glycine/chitosan(Gly/CS)membrane piezoelectric composite material [61]. Copyright 2020, ACS; (c)Gold nanoparticles modified barium titanate nanocube(Au@BTO)piezoelectric composite material [62], Copyright 2021, Elsevier |
图5 生物压电材料:(a)二苯丙氨酸(FF)膜[65];(b)甘氨酸-聚乙烯醇复合薄膜[66] ;(c)跨膜蛋白ba3细胞色素c氧化酶晶体结构[68];(d)β-甘氨酸纳米晶膜[67]Fig. 5 Bio-piezoelectric materials:(a)diphenylalanine (FF) membrane [65], Copyright 2022, Elsevier; (b)Glycine - polyvinyl alcohol composite film [66], Copyright 2021, IEEE;(c)crystal structure of the transmembrane protein ba3 cytochrome c oxidase [68], Copyright 2023, Advanced Functional Materials; (d)β-glycine nanocrystalline film [67], Copyright 2023, Springer Nature |
图8 流行疾病检测:(a)可穿戴压电生物传感器检测病毒颗粒[105];(b)艾滋病病毒检测[109];(c)基孔肯雅病毒检测[111]Fig. 8 Epidemic disease detection:(a)wearable piezoelectric biosensor detection of virus particles [105], Copyright 2021, IEEE; (b)HIV detection [109], Copyright 2016, Elsevier; (c)CHIKV detection [111], Copyright 2023, Macromolecular Symposia |
| [1] |
(吴礼光, 刘茉娥, 朱长乐. 化学进展, 1995, 7(4):287.).
|
| [2] |
(陈玲. 传感器与微系统, 2006, 25(9):4.).
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
(徐秀明, 王俊德, 李海洋. 化学进展, 2005, 17(5):876).
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
(陈令新, 关亚风, 杨丙成, 申大忠. 化学进展, 2002, 14(1): 69.).
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
(裴先茹, 高海荣. 安徽化工, 2010, 36(03): 4.).
|
| [22] |
(刘洋, 汪尧进. 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50(3): 625.).
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
(陈广州, 陈刚, 潘莉, 白智健, 陈东升. 微纳电子技术, 2022, 59(3): 236.).
|
| [28] |
(王嘉程, 王丽坤, 仲超. 电子元件与材料, 2021, 40(3): 219.).
|
| [29] |
(代香林, 姚喜军, 张文凤, 商佳琪, 邓久鹏. 生物医学工程研究, 2021, 40(4): 455.).
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
(马惠铖. 科技资讯, 2010, (30): 119.).
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
(方震, 白忠瑞, 陈贤祥, 夏攀, 何征岭, 赵荣建. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43(5): 1472.).
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
(张奔, 徐磊, 张淑洁, 王大伟. 天津纺织科技, 2022, (1): 44.).
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
Abdullah,
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |