

Environmental Microplastic Pollution Risks Associated with Plastic Waste Landfilling
Received date: 2024-07-10
Revised date: 2024-11-07
Online published: 2025-01-20
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42177377)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(42477413)
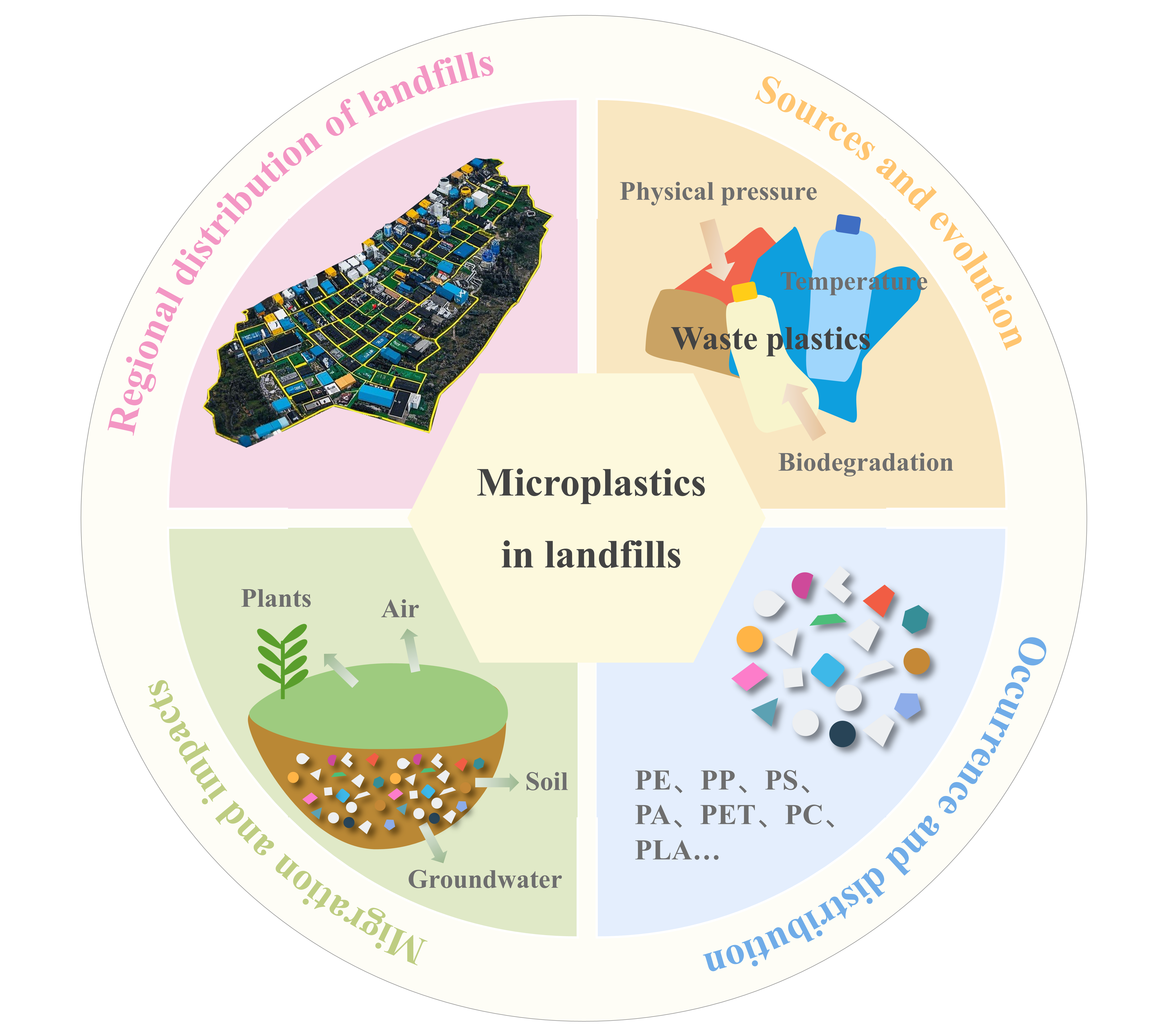
Microplastic pollution arising from the aging and decomposition of plastic waste poses a significant challenge to global plastic pollution control. Landfills have been the primary disposal sites for solid waste for a long time, and the considerable amount of plastic waste accumulated in landfills has emerged as a crucial source of microplastics in terrestrial ecosystems. This paper mainly reviews the development of plastic waste landfilling and its evolution in the landfilling process, analyzes the external input and internal generation process of microplastics in landfills, and summarizes the abundance and structural composition characteristics of microplastics reported in the landfill piles (580-168 000 items/kg) and leachate (420-291 000 items/m3) and the surrounding soils (4-14 200 items/kg) and groundwater (3000-27 200 items/m3). This paper further reveals the migration of microplastics within the waste-soil-groundwater system, and the exposure routes of humans to microplastics through the contaminated soil, air, and edible plants. As the risks and control measures to the entire environmental process of microplastics in landfills urgently require investigation, this paper puts forward key scientific and technical issues and management suggestions.
1 Introduction
2 Distribution and lifecycle of landfills
2.1 Development and distribution of landfills
2.2 Full lifecycle of landfills
3 Sources and evolution of plastics in landfills
3.1 Primary sources of landfill plastic waste
3.2 Fragmentation of landfilled plastic waste
4 Occurrence and distribution of microplastics in landfills
4.1 Microplastics in waste piles
4.2 Microplastics in leachates
5 Migration and impacts of microplastics in landfills
5.1 Microplastic spread to the environment
5.2 Microplastic transfer to plants
6 Perspectives
Hang Liu , Yu Su , Yutao Cheng , Ziyang Lou , Cheng Peng , Jie Wang , Yanhua Wang , Lei Wang , Rong Ji . Environmental Microplastic Pollution Risks Associated with Plastic Waste Landfilling[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2025 , 37(1) : 32 -45 . DOI: 10.7536/PC240712
Figure 1 Global solid waste (a) composition and (b) treatment methodsFig. 1 (a) Composition and (b) disposal approaches of global solid waste |
Table 1 Per capita GDP, per capita output of waste plastics and recovery rate in some countries[5]Table 1 Per capita GDP, per capita generation and recycling rate of plastic waste in selected countries[5] |
| Country | Per capita GDP (USD) | Per capita generation of plastic waste (kg) | Recycling rate of plastic waste (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | 46 445 | 81.0 | 56.1 |
| Austria | 50 137 | 34.1 | 53.8 |
| United Kingdom | 32 980 | 40.0 | 52.2 |
| Switzerland | 81 993 | 100.0 | 49.7 |
| Republic of South Korea | 31 846 | 98.2 | 53.7 |
| Australia | 55 060 | 53.0 | 11.5 |
Figure 2 Abundance (a, c) and particle size distribution (B, d) of microplastics in different landfills and leachate reported in the literatureFig. 2 The abundance (a, c) and size distribution (b, d) of microplastics in the landfilled waste and leachate samples as reported in the literature |
 8 μ g/L), sulfamethazine (3. 9~8. 5 μ g/L), ciprofloxacin (0~434. 7 μ g/L), enrofloxacin (0~9. 1 μ g/L) and erythromycin (8. According to a large number of research results on the adsorption behavior of microplastics to organic substances or heavy metals[62-63]The microplastics in landfill leachate will inevitably interact with coexisting pollutants to form compound pollution through a variety of mechanisms (such as hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding, π - π interaction, electrostatic interaction and pore filling, etc.). However, it is still unclear what exogenous pollutants are contained in the micro plastics in landfill leachate, as well as the concentration and distribution of various pollutants. Due to the high fluctuation of leachate quality, the adsorption of pollutants by microplastics will be affected by many factors, including the structural properties of microplastics (such as particle size[64]Aging degree[65], crystallinity[66]Surface functional group[67]Hydrophobicity and electrification of organic pollutants[68]And environmental factors (pH, temperature, natural organic matter and ionic strength[69]The interface behavior between microplastics and other pollutants will be affected to varying degrees.
8 μ g/L), sulfamethazine (3. 9~8. 5 μ g/L), ciprofloxacin (0~434. 7 μ g/L), enrofloxacin (0~9. 1 μ g/L) and erythromycin (8. According to a large number of research results on the adsorption behavior of microplastics to organic substances or heavy metals[62-63]The microplastics in landfill leachate will inevitably interact with coexisting pollutants to form compound pollution through a variety of mechanisms (such as hydrophobic interaction, hydrogen bonding, π - π interaction, electrostatic interaction and pore filling, etc.). However, it is still unclear what exogenous pollutants are contained in the micro plastics in landfill leachate, as well as the concentration and distribution of various pollutants. Due to the high fluctuation of leachate quality, the adsorption of pollutants by microplastics will be affected by many factors, including the structural properties of microplastics (such as particle size[64]Aging degree[65], crystallinity[66]Surface functional group[67]Hydrophobicity and electrification of organic pollutants[68]And environmental factors (pH, temperature, natural organic matter and ionic strength[69]The interface behavior between microplastics and other pollutants will be affected to varying degrees.| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
Encyclopedia of China. History of Landfill Development, [2024-07-01]. https://www.zgbk.com/ecph/words?SiteID=1&ID=108229.
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
National Bureau of Statistics. 2022 China Municipal Solid Waste Sanitary Landfill, [2024-07-01]. https://data.stats.gov.cn/easyquery.htm?cn=C01&zb=A0C06&sj=2022.
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. 2021 Report on the Status of China's Marine Ecological Environment, (2022-05-27). [2024-07-01]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/jagb/202205/P020220527579939593049.pdf.
|
| [27] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Action Plan for Plastic Pollution Control of the 14th Five-Year Plan, (2021-09-08). [2024-07-01]. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-09/16/content_5637606.htm.
|
| [28] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. Coastal City Marine Debris Cleanup Action Plan, (2024-06-11). [2024-07-01]. https://www.gov.cn/lianbo/bumen/202406/content_6956621.htm.
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
(谭学军, 王磊. 中国给水排水, 2022, 14: 1.).
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
Nurhasanah,
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
(林文琪, 郭子成. 四川环境, 2020, 39(3): 115.).
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |