

Biomass-Based Ionic Thermoelectric Devices
Received date: 2024-03-20
Revised date: 2024-06-05
Online published: 2024-06-30
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22308210)
Scientific Research Program Funded by Shaanxi Provincial Education Department(23JK0350)
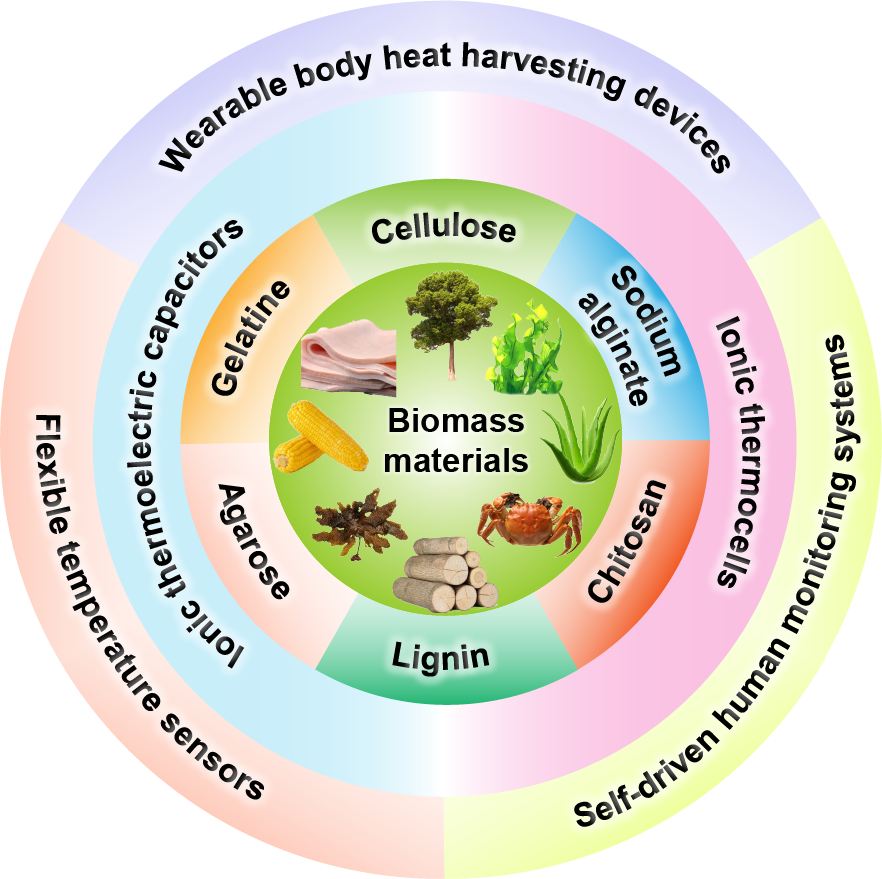
The new ionic thermoelectric material based on biomass has the advantages of high ionic Seebeck coefficient, good flexibility, low cost, green biodegradability, etc., and has broad application prospects in the construction of safe, stable, and efficient flexible wearable thermoelectric devices. In this paper, the preparation methods, thermoelectric principles, and thermoelectric properties of ionic thermoelectric capacitors and ionic thermocells based on biomass materials such as cellulose and gelatin and their latest applications in wearable body heat collection devices, flexible temperature sensors, and self-driven human monitoring systems in the past five years are reviewed. Combined with the current research, we further summarize the difficulties and shortcomings in the research of biomass-based ionic thermoelectric materials, as well as the difficulties and challenges facing the future promotion and application of biomass-based thermoelectric devices. Finally, we propose targeted solution ideas for the existing problems, providing important theoretical guidance and technical references for related research in this field.
1 Introduction
2 Ionic thermoelectric overview
2.1 Thermoelectric materials
2.2 Ionic thermoelectric effect
2.3 Ionic thermoelectric properties examination index
3 Research progress in biomass-based ionic thermoelectric devices
3.1 Biomass materials overview
3.2 Preparation of biomass-based ionic thermoelectric materials
3.3 Design of biomass-based ionic thermoelectric components
3.4 Functional applications of biomass-based ionic thermoelectric devices
4 Conclusion and outlook
Sai Zheng , Xiaoyu Guan , Bingyuan Zhang , Yanxia Zhu , Dongping Li , Qingxin Han , Xuechuan Wang . Biomass-Based Ionic Thermoelectric Devices[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2024 , 36(12) : 1915 -1928 . DOI: 10.7536/PC240322
表1 基于热扩散效应的生物质基离子热电材料的热电性能概括Table 1 Summary of thermoelectric properties of biomass-based ionic thermoelectric materials based on thermal diffusion effect |
| Base material | Transmit ions | Seebeck mV/K | Ionic conductivity S/m | Heat conductivity W/(m·K) | ZT | year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cellulose | NaOH | 24 | — | 0.48±0.03 | — | 2019[55] |
| CMC-Na | NaCl | 17.1 | 2.68 | — | — | 2021[47] |
| BC | [EMIm]DCA | 18.04 | 2.88 | 0.21 | 1.33 | 2021[59] |
| BC | NaCl | −27.2 | 20.42 | 0.318 | — | 2022[95] |
| GEL | [EMIm]DCA | 2.83 | 2.29 | — | — | 2022[93] |
| CS/PVA | CuCl2 | −28.4 | 4.05 | 0.487 | 2.42 | 2023[84] |
| AG | Na:DBS | 41.8 | 0.0182 | — | — | 2023[80] |
| SA/PVA/PEG | NaBF4 | 66.7 | 3.14 | — | — | 2023[88] |
| Lignin/PVA | KOH | 5.71 | 5.15 | 0.195 | 0.25 | 2023[76] |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |