

Application of Nanozymes in the Treatment of Brain Diseases
Received date: 2023-05-10
Revised date: 2023-06-19
Online published: 2023-08-06
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(82103147)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(12272253)
Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, China(20210302124007)
Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province, China(202203021221047)
Shanxi-Zheda Institute of Advanced Materials and Chemical Engineering(2021SX-AT008)
Shanxi-Zheda Institute of Advanced Materials and Chemical Engineering(2021SX-AT009)
In recent years, nanozymes, as a new generation of artificial enzymes, have gradually entered the medical field due to their multi-enzyme activity, high stability and targeting ability, which are superior to natural enzymes. Moreover, nanozymes have been applied to the treatment of a variety of diseases and cancer because of their regulatory effect on reactive oxygen species. Brain diseases, as one of the highest mortality diseases, are prone to produce complex inflammatory responses due to excessive reactive oxygen species in the pathological environment. Therefore, the application of nanozymes in the brain environment may become an effective means of monitoring and treatment of brain diseases. This article reviews the principles of nanozymes in the treatment of brain diseases and the current research status in this field in recent years, including nanozymes inducing cancer cell death by regulating the level of reactive oxygen species, nanozymes assisting traditional anticancer therapy, nanozymes using membrane proteins to monitor brain cancer, and their applications in traumatic brain injury, stroke, brain degenerative diseases, cerebral malaria and epilepsy. At the end of this text, the problems of its application in clinical treatment are discussed.
1 Introduction
2 Development of researches about nanozymes
3 Application of nanozymes in the treatment of brain cancer and brain diseases
3.1 Nanozymes in brain cancer
3.2 Nanozymes in degenerative disease
3.3 Nanozymes in other brain diseases
4 Conclusion and outlook
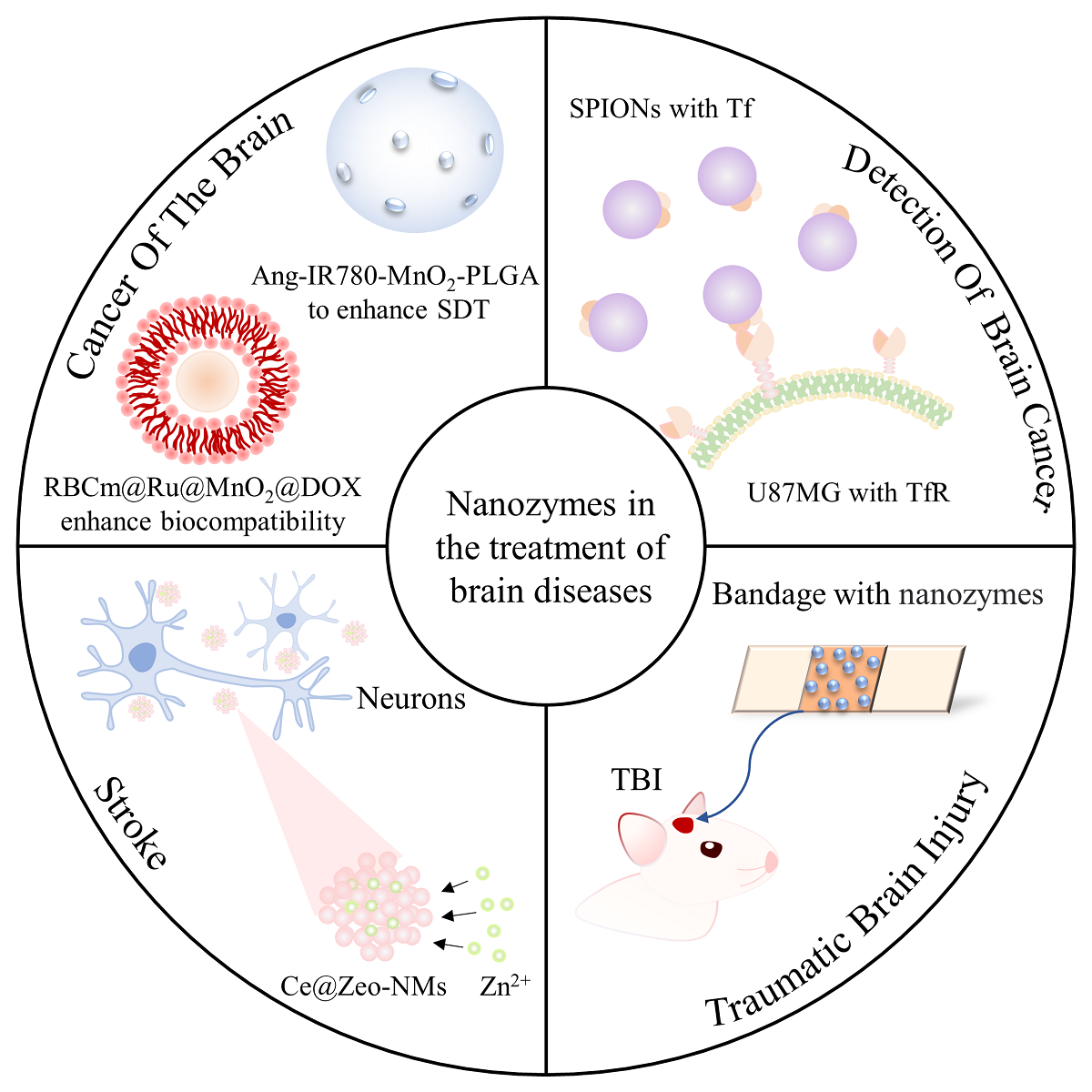
Key words: nanozymes; ROS; brain cancer; brain injury; Alzheimer’s disease
Ziying Meng , Jie Wang , Jiapu Wang , Yan Wei , Di Huang , Ziwei Liang . Application of Nanozymes in the Treatment of Brain Diseases[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2024 , 36(1) : 18 -26 . DOI: 10.7536/PC230507
表1 部分纳米酶较天然酶的优点[15⇓⇓⇓~19]Table 1 Advantages of some nanozymes compared with native enzymes[15⇓⇓⇓~19] |
| Types | Advantage | ref |
|---|---|---|
| Graphene and its derivatives | Large specific surface areas; rich surface chemistry | 15 |
| CeO2 nanoparticles | Multiple catalytic activities | 15 |
| BSA-Au cluster | Good stability and high biocompatibility in water solution | 16 |
| FeN3P-SAzyme | Comparable peroxidase-like catalytic activity and kinetics to natural enzymes | 17 |
| Boron-doped Fe-N-C single-atom nanozymes | Vivid mimicking nature peroxidase | 18 |
| MNx | Efficient multienzyme-mimetic catalysis with good selectivity; 4 and 5-fold higher affinities in peroxidase-like activity than the FeN4 and natural horseradish peroxidase; Higher affinity in the catalase-like activity | 19 |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
(侯亚欣, 张若飞, 阎锡蕴, 范克龙. 中国科学(生命科学), 2020, 50(3): 311.)
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
(高利增, 梁敏敏, 温涛, 魏辉, 张宇, 范克龙, 江冰, 曲晓刚, 顾宁, 庞代文, 许海燕, 阎锡蕴. 中国科技术语, 2020, 22(06): 21.)
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
(高利增, 陈雷, 张若飞, 阎锡蕴. 中国科学:化学, 2022, 52(09): 1649.)
|
| [25] |
(范克龙, 高利增, 魏辉, 江冰, 王大吉, 张若飞, 贺久洋, 孟祥芹, 王卓然, 樊慧真, 温涛, 段德民, 陈雷, 姜伟, 芦宇, 蒋冰, 魏咏华, 李唯, 袁野, 董海姣, 张鹭, 洪超仪, 张紫霞, 程苗苗, 耿欣, 侯桐阳, 侯亚欣, 李建茹, 汤国恒, 赵越, 赵菡卿, 张帅, 谢佳颖, 周子君, 任劲松, 黄兴禄, 高兴发, 梁敏敏, 张宇, 许海燕, 曲晓刚, 阎锡蕴. 化学进展, 2023, 35(01): 1.).
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |