

Design and Structure Regulation of VOCs Catalytic Oxidation Catalysts
Received date: 2023-06-08
Revised date: 2023-08-30
Online published: 2024-01-05
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation Program of China(22306210)
National Key Research & Development Program of China(2022YFB3504004)
SINOPEC RIPP Project(PR20230115)
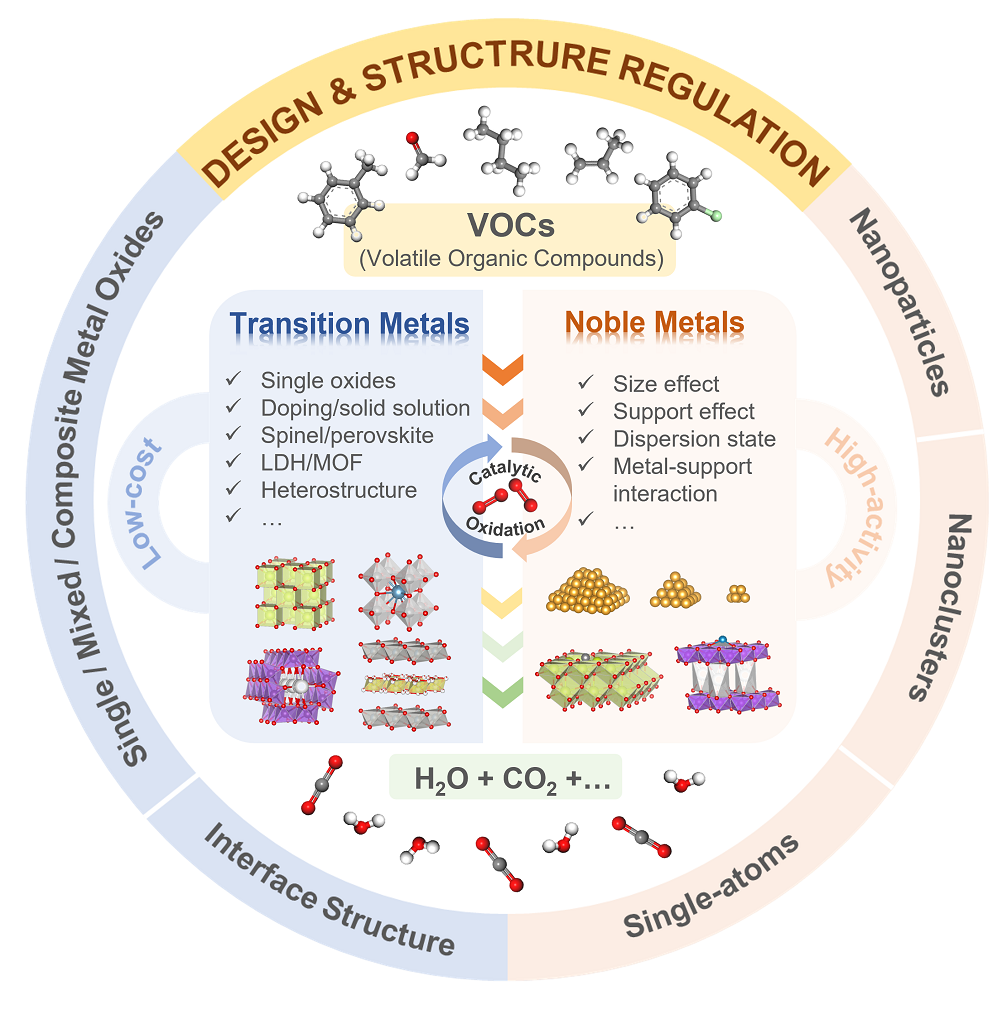
In recent years, with the improvement of the air quality in China, traditional pollutants such as NOx and SO2 have been effectively controlled. The emission control of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) has gradually become a key to further alleviating the regional composite air pollution so far. Catalytic oxidation is one of the most promising VOCs emission reduction technologies due to its high treatment efficiency, low energy consumption, and wide applicability. The development of high-performance catalysts is crucial for this technology. The design and structural regulation of catalysts associated with mechanism study is currently a research hotspot. This paper first outlines the catalytic oxidation mechanism of VOCs. Secondly, the research progress on the structural regulation of non-noble metal catalysts is reviewed from the perspectives of single transition metal oxides, mixed metal oxides, composite metal oxides, and interface structure regulation. Based on the dispersion state, the size effect and support effect of noble metal nanoparticles/clusters in noble metal catalysts are summarized. The regulation strategies based on the metal-support interaction for the emerging single-atom catalysts are also discussed. Finally, this paper provides a summary and prospects for future research trends. We believe that based on deeply clarifying the structure-activity relationship, developing simple and refined structure regulation methods of catalysts and adapting to actual operating conditions and industrial scale-up is the focus of future research.
1 Introduction
2 VOCs catalytic oxidation mechanisms
3 Structure regulation of non-noble metal catalysts
3.1 Single transition metal oxides
3.2 Mixed transition metal oxides
3.3 Composite transition metal oxides
3.4 Interface structure regulation
4 Regulation of metal dispersion state in noble metal catalysts
4.1 Noble metal nanoparticle/cluster catalysts
4.2 Noble metal single-atom catalysts
5 Conclusion and outlook
Wenhao Yang , Dongyue Zhao , Haitao Song , Junhua Li . Design and Structure Regulation of VOCs Catalytic Oxidation Catalysts[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2024 , 36(1) : 27 -47 . DOI: 10.7536/PC230604
图4 (a)δ-MnO2不同层间离子掺杂对甲醛及其氧化中间物种吸附能的影响[43],(b)MOF-71衍生Co-Ce混合氧化物及其丙酮氧化活性[73]Fig. 4 (a) The effect of different interlayer ions in δ-MnO2 on the adsorption energy of formaldehyde and oxidation intermediate species[43], Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society; (b) MOF-71-derived Co-Ce mixed oxides and their acetone oxidation activity[73], Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society |
图10 (a)Pd负载于不同形貌CeO2表面时其CO与丙烷氧化反应速率[152],(b)MOF原位生长诱导Co3O4与Pt NPs间电子转移促进甲苯氧化机理示意图[153]Fig. 10 (a) The reaction rate of CO and propane oxidation over Pd loaded on CeO2 with different morphologies[152], Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society; (b) Schematic diagram of electron transfer between Co3O4 and Pt NPs induced by MOF in situ growth promoting toluene oxidation[153], Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society |
图12 (a)H2O2辅助MnO2表面Mn空位捕获Ag单原子促进氧活化[179];(b)Co3+位点稳定Ag单原子促进苯氧化[180]Fig. 12 (a) H2O2-assisted Mn vacancy capture of Ag single atom on MnO2 surface promoting oxygen activation[179], Copyright 2022, Royal Society of Chemistry; (b) Co3+-site stabilized Ag single atom promoting benzene oxidation activity[180], Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People's Republic of China. 2021 China Ecological Environment Status Bulletin[EB/OL]. (2022-05-27)[2023-05-17]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202205/P020220608338202870777.pdf.
(中华人民共和国生态环境部. 2021中国生态环境状况公报[EB/OL]. (2022-05-27) [2023-05-17]. https://www.mee.gov.cn/hjzl/sthjzk/zghjzkgb/202205/P020220608338202870777.pdf.)
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
(李俊华, 姚群, 朱廷钰. 工业烟气多污染物深度治理技术及工程应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019. ).
|
| [7] |
(叶代启. 工业挥发性有机物的排放与控制. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.).
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
| [152] |
|
| [153] |
|
| [154] |
|
| [155] |
|
| [156] |
|
| [157] |
|
| [158] |
|
| [159] |
|
| [160] |
|
| [161] |
|
| [162] |
|
| [163] |
|
| [164] |
|
| [165] |
|
| [166] |
|
| [167] |
|
| [168] |
|
| [169] |
|
| [170] |
|
| [171] |
|
| [172] |
|
| [173] |
|
| [174] |
|
| [175] |
|
| [176] |
|
| [177] |
|
| [178] |
|
| [179] |
|
| [180] |
|
| [181] |
|
| [182] |
|
| [183] |
|
| [184] |
|
| [185] |
|
| [186] |
|
| [187] |
|
| [188] |
|
| [189] |
|
| [190] |
|
| [191] |
|
| [192] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |