

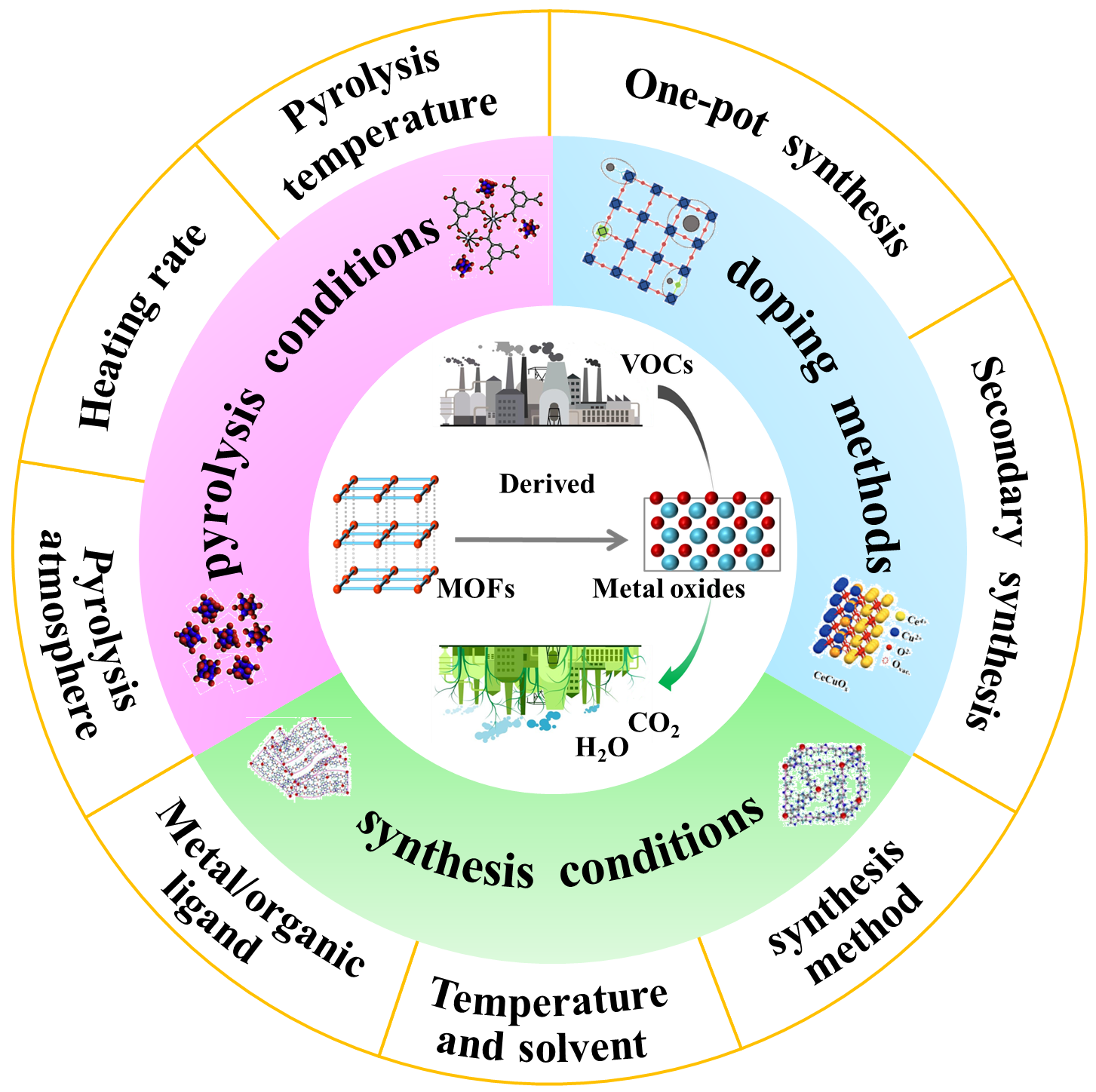
Application of MOFs-Derived Metal Oxides in Catalytic Total Oxidation of VOCs
Received date: 2023-05-11
Revised date: 2023-07-11
Online published: 2023-08-06
Supported by
Chongqing Technical Innovation and Application Development Special Surface Project(cstc2020jscx-msxmX0071)
Chongqing Technical Innovation and Application Development Special Surface Project(CSTB2022TIAD-GPX0033)
Science and Technology Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission(KJZD-K202300709)
The emission of a significant amount of VOCs has resulted in severe impacts on both human health and the environment. Currently, the most effective method for treating VOCs is their total oxidation to carbon dioxide and water through metal oxide catalysis. To enhance the catalytic performance of metal oxides, various synthetic strategies have been developed, including morphology, defect, and doping engineering. However, these processes are cumbersome and require further improvements to enhance the catalytic performance. On the other hand, metal-organic frameworks (MOFs)-derived metal oxides have been extensively used to catalyze the complete oxidation of VOCs. This is because of their tunable morphology, large specific surface area, high defect concentration, and excellent doping dispersion. However, there is a lack of a comprehensive summary of the application of MOFs-derived metal oxides in the total oxidation of VOCs. Therefore, this paper reviews the synthesis conditions, doping methods, and pyrolysis conditions of MOFs from the control strategy of derived metal oxides. It also summarizes the regulation methods and the relationship between the physicochemical properties of derived metal oxides and the total oxidation performance of VOCs. Additionally, this paper discusses the future development and challenges of MOFs-derived metal oxides.
1 Introduction
2 Regulatory strategies of MOFs-derived metal oxides and their application in catalytic total oxidation of VOCs
2.1 Synthesis conditions
2.2 Doping methods
2.3 Pyrolysis conditions
3 Mechanism of catalytic VOCs total oxidation
4 Conclusion and outlook
Tao Peng , Qianqian Chai , Chuanqiang Li , Xuxu Zheng , Lingjuan Li . Application of MOFs-Derived Metal Oxides in Catalytic Total Oxidation of VOCs[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2024 , 36(1) : 81 -94 . DOI: 10.7536/PC230511
表1 近5年来MOFs衍生的MOs在VOCs的研究总结Table 1 Summary of research on MOFs-derived MOs in VOCs in recent five years |
| Catalyst | MOF | pyrolysis conditions | pollutant | Concentration(ppm) | WHSV(mL·gcat−1·h−1) | T90(℃) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2/Co3O4 | CoCe-BDC | Air, 350 ℃ | Acetone | 600 | 18 600 | 180 | 35 |
| CeCoOx-MNS | ZIF-67 | Air, 450 ℃ | Toluene | 3000 | 30 000 | 249 | 44 |
| CeO2-1 | Ce-BTC | Air, 450 ℃ | o-xylene | 500 | 48 000 | 198 | 52 |
| Co3O4-R | Co-MOF-74 | Air, 350 ℃ | o-xylene | 100 | 120 000 | 270 | 37 |
| Mn-100-AR-O | MIL-101(Mn) | O2 after Ar, 700 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 30 000 | 265 | 49 |
| ZSA-1-Co3O4 | ZSA-1 | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | / | 20 000 | 240 | 40 |
| CeO2 | Ce-MOF-808 | Air, 250 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 30 000 | 278 | 41 |
| Mn3O4-MOFs-74-300 | Mn-MOF-74 | Air, 300 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 20 000 | 218 | 50 |
| CeCoOx-200 | Ce[Co(CN)6]2·nH2O | Air, 500 ℃ | Toluene | 3000 | 30 000 | 168 | 56 |
| Co3O4-400 | ZIF-67 | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | 12000 | 21 000 | 259 | 43 |
| CeO2-C | Ce-BTC | Air, 450 ℃ | o-xylene | 500 | 48 000 | 193 | 62 |
| Co2Mn3 | MnCo-BTC | Air, 350 ℃ | Propane | 10000 | 120 000 | 255 | 45 |
| M-Co2Cu1Ox | CoCu-MOF-74 | Air, 400 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 30 000 | 220 | 66 |
| MOF-Mn1Co1 | Mn3[Co(CN)6]2·nH2O | Air, 450 ℃ | Toluene | 500 | 96 000 | 226 | 75 |
| MnOx-CeO2-MOF | Ce/Mn-MOF-74 | Air, 600 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 60 000 | 220 | 78 |
| CuMn2Ox | CuMn -BTC | N2,350 ℃&500 ℃ | Acetone | 1019 | 18 000 | 144 | 80 |
| MnOx-CeO2-s | Mn/Ce-BTC | Air, 600 ℃ | ethylacetate | 500 | 60 000 | 205 | 83 |
| CuO/Co3O4 | Cu/ZIF-67 | Air, 500 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 20 000 | 229 | 84 |
| M-Co1Mn1Ox | Mn/ZSA-1 | Air, 500 ℃ | Toluene | - | 20 000 | 192 | 85 |
| 15Mn/Cr2O3-M | Cr-MIL-101 | Air, 500 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 60 000 | 268 | 86 |
| 10%CeO2-MnOx | Mn-BTC | Air, 300 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 48 000 | 275 | 89 |
| M-Co1Cu1Ox | Mn/ZSA-1 | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 20 000 | 208 | 88 |
| MnOx/Co3O4-4 h | Mn/ZIF-67 | Air, 350 ℃ | chlorobenzene | 1000 | 60 000 | 334 | 90 |
| MnOx/Co3O4-10 | Mn/ZIF-67 | O2 after N2, 500 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 120 000 | 242 | 70 |
| CoMn6 | Mn/ZIF-67 | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 60 000 | 219 | 92 |
| MOF-CMO/400 | Mn3[Co(CN)6]2·nH2O | Air, 400 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 20 000 | 209 | 72 |
| M-Co3O4-350 | ZSA-1 | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 20 000 | 239 | 95 |
| Co3O4-350 | Co-BTC | Air, 350 ℃ | Propane | 10000 | 60 000 | 275 | 96 |
| CeO2-MOF/ 350 | Ce-BTC | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 12 000 | 260 | 97 |
| 1Mn1Ce-300 | MnCe-BTC | O2 after Ar, 300 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 30 000 | 244 | 103 |
| HW-MnxCo3-xO4 | ZIF-67 | Air, 350 ℃ | Toluene | 3000 | 30 000 | 188 | 104 |
| MnOx-NA | Mn-BDC | O2 after N2, 350 ℃ | Acetone | 600 | 56 000 | 167 | 105 |
| MnOx@ZrO2-NA | MOF-808 | O2 after N2, 300 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 60 000 | 260 | 106 |
| MnOx-700 | Mn-MOF-74 | Air, 700 ℃ | chlorobenzene | 50 | 12 000 | 225 | 109 |
| 3Mn2Ce | Mn/Ce-BTC | O2 after Ar, 300 ℃ | Toluene | 1000 | 30 000 | 236 | 117 |
图1 (a) Co3O4-R和Co3O4-S的形貌及o-xylene上的催化氧化活性[37];(b) ZSA-1-Co3O4、MOF-74-Co3O4和ZIF-67-Co3O4的形貌以及甲苯完全氧化活性[40];(c) Ce-MOF-808、Ce-BTC、Ce-UiO-66的XRD图谱[41];(d) DMF/水控制Co-MOF-74尺寸和形貌的机制[42];(e) 1.7 μm、800 nm和400 nm尺寸ZIF-67的合成过程[43];(f) 立方状、网状纳米片、棒状的Co-MOFs的合成步骤[44];(g)球磨法制备MOFs衍生MnCo二元氧化物的示意图[45]Fig. 1 (a) Morphology of Co3O4-R and Co3O4-S and catalytic oxidation activity on o-xylene[37]; (b) Morphology of ZSA-1-Co3O4, MOF-74-Co3O4 and ZIF-67-Co3O4 and complete oxidation activity of toluene[40]; (c) XRD patterns of Ce-MOF-808, Ce-BTC and Ce-UiO-66[41]; (d) Mechanism of DMF/ water control on the size and morphology of Co-MOF-74[42]; (e) Synthesis of ZIF-67 at 1.7 μm, 800 nm and 400 nm[43]; (f) Synthesis steps of cubic, reticular nanosheet and rod-like Co-MOFs[44]; (g) Schematic diagram of preparation of MoFs-derived MnCo dioxides by ball milling[45] |
图2 (a) CoCeBDC衍生的CoCeOx和普通负载制备Co3O4/CeO2[68];(b) CeCuBDC衍生的异价取代的CeCuOx[67];(c) MOFs的掺杂位点[33];(d) 硝酸镍掺杂ZIF-67制备中空NiOx/Co3O4的流程[69];(e) 协同热解-氧化-吸附制备MnOx/Co3O4的过程[70];(f) Co-MOFs封装到有序介孔CeO2中制备CeCoOx的流程[71];(g) 中空CoMn2O4的制备方法[72]Fig. 2 (a) Co3O4/CeO2 was prepared by CoCeOx derived from CoCeBDC and ordinary load[68]; (b) CoCeBDC derived heterovalent substituted CoCeOx[67]; (c) Doping sites of MOFs[33]; (d) Preparation of hollow NiOx/Co3O4 by doping ZIF-67 with nickel nitrate[69]; (e) The preparation of MnOx/Co3O4 by synergistic pyrolysis-oxidation-adsorption[70]; (f) CeCoOx was prepared by encapsulation of Co-MOFs into ordered mesoporous CeO2[71]; (g) Preparation method of hollow CoMn2O4[72] |
图3 (a) 不同温度下热解Ce-BTC的图解模型[99];(b) ZIF-67在不同热解条件下的形貌图解[104];(c) 两段式制备MnOx-NA的过程[105];(d) 两段式制备MnOx@ZrO2-NA的过程[106]Fig. 3 (a) Graphical models of pyrolysis Ce-BTC at different temperatures[99]; (b) Morphology diagram of ZIF-67 under different pyrolysis conditions[104]; (c) Two-stage preparation of MnOx-NA[105]; (d) A two-stage process for preparing MnOx@ZrO2-NA[106] |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |