

Selective Ionic Removal Strategy and Adsorbent Preparation
Received date: 2022-10-14
Revised date: 2023-03-20
Online published: 2023-04-30
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(22176015)
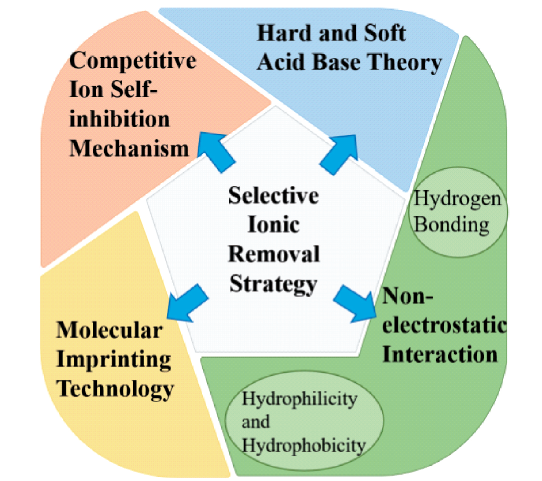
The selective ionic removal from water or wastewater by newly-developed adsorbents has been intensely investigated around the world since 1960s. These selective ionic adsorbents were used to control the concentrations of specific ions in drinking water or wastewater in the presence of plentiful coexisting ions to prepare quality drinking water or avoid ecological hazards in natural waterbodies due to wastewater discharge. Due to remarkable market demands and wide application prospects, this topic still generates numerous amazing findings in terms of international publications in recent decade. Besides the history, the present status and the research bias, this paper lays particular emphasis on the four selective ionic removal strategies involved in previous studies (i.e., the molecular imprinting technology, the soft and hard acid base theory, the non-electrostatic interaction theory, and the self-inhibition theory of competitive ions), including their mechanisms, histories, and adsorbent preparations and applications. Finally, this review also prospects the future research directions. This review provides overall information for the further development of selective ionic adsorbents for water or wastewater treatment.
1 Introduction
2 Selective ion adsorption materials based on molecular imprinting technology
2.1 Principles and development history of molecular imprinting technology
2.2 Preparation of molecularly imprinted materials and selective ion adsorption
3 Selective ion adsorption materials based on hard and soft acid base theory
3.1 The development history of acid-base theory
3.2 Preparation of hard and soft acid base materials and selective ion adsorption
4 Selective anion adsorption materials based on non-electrostatic interaction
4.1 Selective ion adsorption based on hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity
4.2 Selective ion adsorption based on hydrogen bonding
5 Selective ion adsorption of standard resin based on competitive ion self-inhibition mechanism
6 Conclusion and outlook
Key words: selective ionic removal; strategy; water treatment; adsorbent
Zhixuan Wang , Shaokui Zheng . Selective Ionic Removal Strategy and Adsorbent Preparation[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2023 , 35(5) : 780 -793 . DOI: 10.7536/PC221005
图1 2018—2022年(8月)选择性离子吸附材料领域国际论文发表情况Fig. 1 Number of international publications on selective ionic materials during 2018—2022 (August) |
图4 GO-IIP的XPS图谱:(a) 吸附Pb(Ⅱ)前后的调查图谱;(b) Pb(Ⅱ)吸附后的Pb 4f光谱;吸附前(c)和吸附后(d)的N 1s谱;吸附前(e)和吸附后(f)的O1 s光谱[86]Fig. 4 XPS spectra of GO-IIP: (a) survey spectra before and after Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption; (b) Pb 4f spectrum after Pb(Ⅱ) adsorption; N 1 s spectra before adsorption (c) and after adsorption (d); O1 s spectra before adsorption (e) and after adsorption (f)[86] |
| Base | Absolute hardness ( ) | Base | Absolute hardness ( ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| F- | 7.0 | CN- | 5.3 |
| Cl- | 4.7 | SH- | 4.1 |
| Br- | 4.2 | ClO- | 4.5 |
| I- | 3.7 | CO- | 6.0 |
| 5.3 | H2O | 7.0 | |
| OH- | 5.6 | H2S | 5.3 |
| NO- | 4.5 | NH3 | 6.9 |
| Acid | Absolute hardness ( ) | Acid | Absolute hardness ( ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| H+ | ∞ | Zn2+ | 10.8 |
| Li+ | 35.1 | Hg2+ | 7.7 |
| Na+ | 21.1 | Pb2+ | 8.5 |
| Rb+ | 11.7 | Ba2+ | 12.8 |
| Cu+ | 6.3 | Pd2+ | 6.8 |
| Ag+ | 6.9 | Cd2+ | 10.3 |
| Au+ | 5.7 | Al3+ | 45.8 |
| Mg2+ | 32.5 | Sc3+ | 24.6 |
| Ca2+ | 19.7 | Fe3+ | 13.1 |
| Ti2+ | 7.0 | La3+ | 15.4 |
| Mn2+ | 9.3 | I2 | 3.4 |
| Fe2+ | 7.3 | Cl2 | 4.5 |
| Ni2+ | 8.5 | CO2 | 6.9 |
| Cu2+ | 8.3 | SO2 | 5.6 |
| Type | Ions |
|---|---|
| Soft acid | Pd2+, Pt2+, Pt4+, Cu+, Ag+, Cd2+, Hg2+, Br2, I2 |
| Borderline acid | Fe2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Zn2+, Ru3+, Sn2+, Pb2+, Sb2+ |
| Hard acid | H+, Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Sr2+, Sc3+, La3+, Ce4+, Zr4+ |
| Soft base | H-, C2H4, C6H6, CN-, SCN-, R3P |
| Borderline base | C6H5NH2, C5H5N, , , Br- |
| Hard base | NH3, N2H4, OH-, , , , , , , F- |
| [1] |
Environmental Quality Standard for Surface Water (GB3838-2002). Beijing: Genetal Bureau of China National Environment Protection, 2002.
(地表水环境质量标准(GB 3838-2002). 北京: 中国国家环境保护总局, 2002.).
|
| [2] |
Standards for Drinking Water Quality(GB 5749-2022). Beijing: State Administration for Market Regulation, Standardization Administration, 2022.
(生活饮用水卫生标准(GB 5749-2022). 北京: 国家市场监督管理总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会, 2022.).
|
| [3] |
Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard(GB 8978-1996). Beijing: National Environmnent Protection Bureau, State Technology Supervision Bureau, 1996.
(污水综合排放标准(GB 8978-1996). 北京: 国家环境保护总局, 国家技术监督局, 1996.).
|
| [4] |
(王方. 现代离子交换与吸附技术. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015.).
|
| [5] |
(何炳林. 离子交换与吸附树脂. 上海: 上海科技教育出版社, 1995.1.).
|
| [6] |
((日)清水博(著). 许景文(编译). 离子交换树脂. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1960.1).
|
| [7] |
(邵林. 水处理用离子交换树脂. 北京: 水利电力出版社, 1989. ).
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
(于晓洋, 罗亚楠, 杨艳艳, 金华, 任红. 山东化工. 2017, 46(24): 71.).
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
| [109] |
|
| [110] |
|
| [111] |
|
| [112] |
|
| [113] |
|
| [114] |
|
| [115] |
|
| [116] |
|
| [117] |
|
| [118] |
|
| [119] |
|
| [120] |
|
| [121] |
|
| [122] |
|
| [123] |
|
| [124] |
|
| [125] |
|
| [126] |
|
| [127] |
|
| [128] |
|
| [129] |
|
| [130] |
(叶明富, 曹云钟, 丁仁浩, 雷智平, 金玲, 张婧. 化工时刊. 2019, 33(02): 28.).
|
| [131] |
|
| [132] |
|
| [133] |
|
| [134] |
|
| [135] |
|
| [136] |
|
| [137] |
|
| [138] |
|
| [139] |
|
| [140] |
|
| [141] |
|
| [142] |
|
| [143] |
|
| [144] |
|
| [145] |
|
| [146] |
|
| [147] |
|
| [148] |
|
| [149] |
|
| [150] |
|
| [151] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |