

Conductive Phase Change Materials (PCMs) for Electro-to-Thermal Energy Conversion, Storage and Utilization
†These authors contributed equally to this work.
Received date: 2022-09-21
Revised date: 2022-11-05
Online published: 2023-02-20
Supported by
Youth Scientific Research Fund of Army Logistics Academy of PLA China(LQ-QN-202117)
National Key Research and Development Program of China(2020YFA0210701)
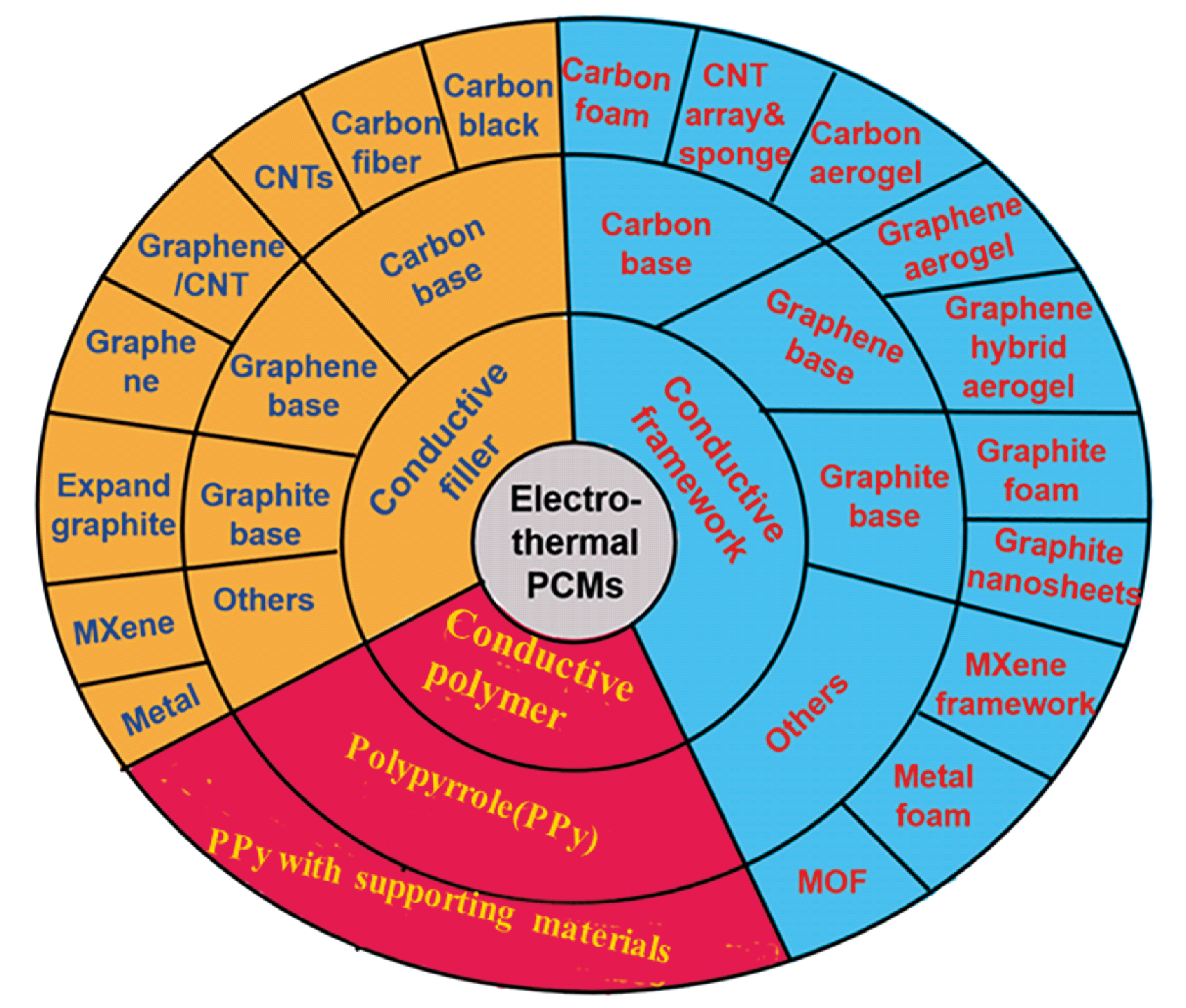
As the largest supply end and demand end in daily production respectively, the conversion, storage and utilization of electric energy and thermal energy play an important role in energy systems. Therefore, it is of great significance to develop high-efficiency materials for electro-thermal conversion and storage, especially facing today’s energy crises, environmental pollution and extreme climates. Among heat storage materials, phase change materials (PCMs) own unique advantages because of their high latent heat storage density and constant temperature during heat absorption and release. However, the low intrinsic conductivity of most PCMs does not match the large power requirements of current energy storage systems. This issue can be effectively improved by combining PCMs with conductive materials to obtain electrically heatable PCM composites. In this article, the latest research progress of electro-thermal conversion PCMs from three aspects of the functional mechanism, affecting factors and applications are systematically reviewed. Moreover, PCMs composited with conductive fillers, conductive framework and serving as conductive polymers are summarized and compared critically. Finally, this article points out the potential direction of future research and emphasizes the key points of this field.
Jiang Haoyang , Xiong Feng , Qin Mulin , Gao Song , He Liuruyi , Zou Ruqiang . Conductive Phase Change Materials (PCMs) for Electro-to-Thermal Energy Conversion, Storage and Utilization[J]. Progress in Chemistry, 2023 , 35(3) : 360 -374 . DOI: 10.7536/PC220922
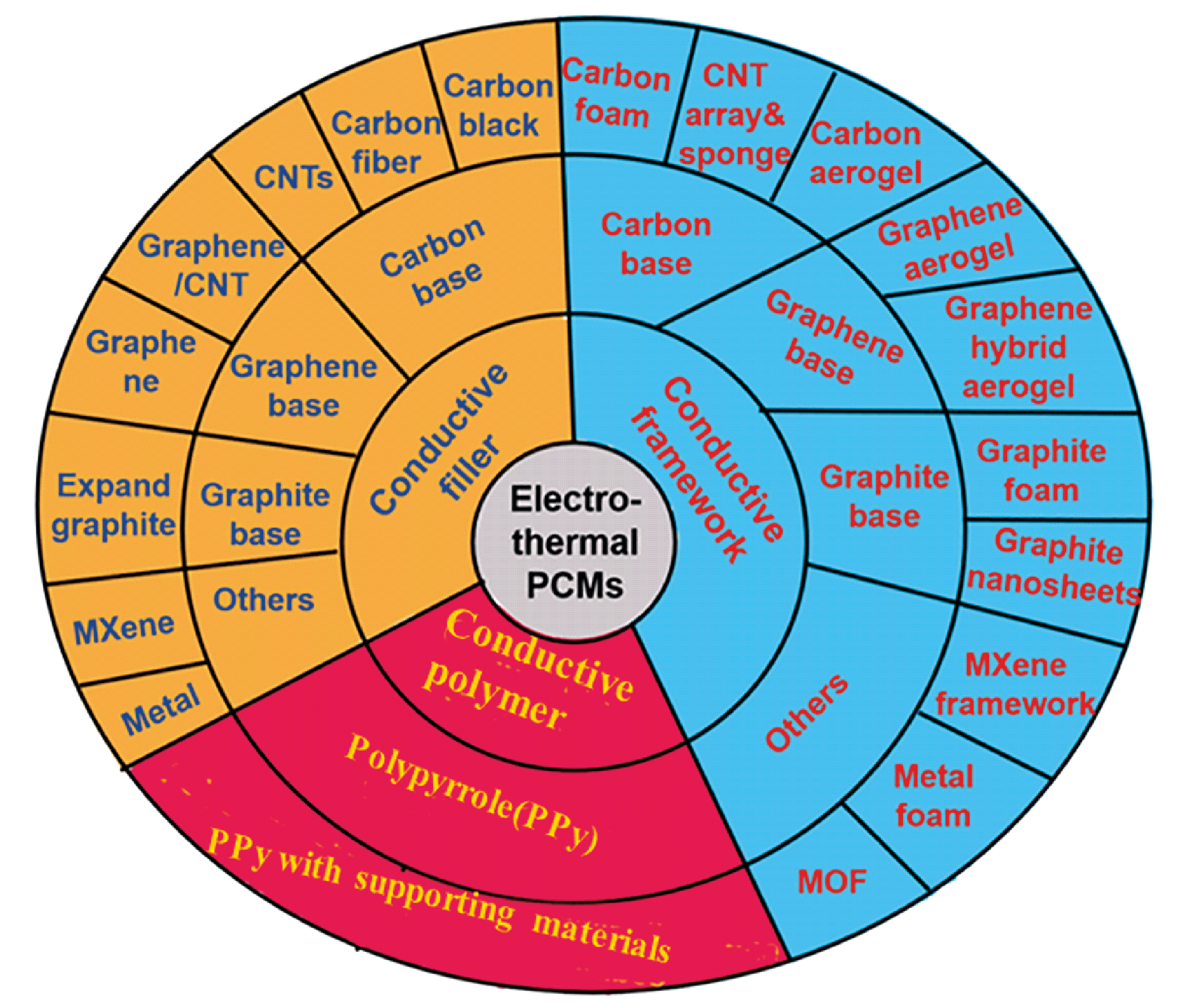
表1 导电填料复合电热相变材料性能Table 1 Properties of conductive filler electrothermal phase change composite |
| Conductive filler | PCMs | Filler content (wt%) | ( ℃) | Latent heat (J/g) | λW/(m·k) | σb (S/m) | The trigger voltagec (V) | ηd (%) | The working voltage e (V) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| acetylene black | PEG2000· CaCl2 | 20 | 51.48 | 78.5 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 29.7 | 1.5 | 15 |
| acetylene black | PEG2000· CaCl2 | 20 | 51.48 | 78.5 | 1.2 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 64.7 | 2.5 | 15 |
| carbon nanofiber | paraffin wax | 2 | 70 | - | - | 0.2 | - | - | - | 16 |
| single-wall CNT | hexadecyl acrylate | - | 36.7 | 52 | 0.4675 | 718 | - | - | - | 17 |
| multi-wall CNT | hexadecyl acrylate | - | 38 | 40 | 0.877 | 389 | - | - | - | 17 |
| CNTs | PEG2000- CaCl2 | 20 | 49.72 | 89.81 | 0.91 | 0.01 | - | 58.3 | 1.5 | 18 |
| CNTs | PEG2000- CaCl2 | 20 | 49.72 | 89.81 | 0.91 | 0.01 | - | 70.2 | 2 | 18 |
| expanded graphite | PEG2000- CaCl2 | 6 | 49.3 | 107.5 | 3.73 | 0.2 | 2 | 48.2 | 2 | 19 |
| expanded graphite | PEG2000- CaCl2 | 6 | 49.3 | 107.5 | 3.73 | 0.2 | 2 | 86.9 | 5 | 19 |
| expanded graphite | Methyl stearate | 15 | 33.4 | 147 | 3.6 | - | 1.4 | 47 | 1.4 | 20 |
| expanded graphite | Methyl stearate | 15 | 33.4 | 147 | 3.6 | - | 1.4 | 72 | 1.7 | 20 |
| expanded graphite | N-eicosane | 15 | 36.41 | 199.4 | 3.56 | - | 1.9 | 65.7 | 2.1 | 21 |
| expanded graphite | N-eicosane | 30 | 36.31 | 163.5 | 4.21 | - | 1.9 | 42.9 | 2.1 | 21 |
| expanded graphite | paraffin | 20 | 56.2 | 120 | 1.38 | 5 | - | - | - | 22 |
| expanded graphite | paraffin | 70 | 43.05 | 47.76 | 19.27 | 4545 | - | - | 4.4 | 23 |
| graphene | Hexadecyl acrylate | - | 32.7 | 57 | 3.957 | 219 | - | - | 30 | 24 |
| graphene oxide/CNT | PEG1000 | 22 | 37.24 | 110.7 | 0.45 | - | 5.8 | 70 | 6.6 | 25 |
| graphene oxide/CNT | docosane | 3.3 | 38.1 | 240.8 | - | 52.63 | - | - | - | 26 |
| graphene/ PANI | PEG20000 | - | 57.93 | 115.97 | - | - | - | - | - | 27 |
| CNT/PU/ PDA/ PEDOT:PSS | paraffin wax | - | 20 | 106.86 | - | - | - | 42.92 | 3 | 28 |
| CNT/PU/ PDA/ PEDOT:PSS | paraffin wax | - | 20 | 106.86 | - | - | - | 91.03 | 4.2 | 28 |
| CNT/PU/Ag nanoflower | Lauric acid | - | 46 | 124.5 | 0.479 | 190 | - | 70.1 | 20 | 29 |
| cotton/ stainless steel wire | PEG | - | 53.53 | 33.46 | 0.281 | - | - | - | - | 30 |
| Ti3C2 MXene nanosheets | PEG4000 | 22.5 | 60 | 131.2 | 2.052 | 10.41 | - | - | 7.2 | 31 |
a The melting point of phase change composites. | |
b The electro conductibility. | |
c The trigger voltage refers to the critical voltage for triggering the complete phase change of the PCM composites. | |
d The electrothermal conversion efficiency. | |
e The working voltage refers to the corresponding voltage of the maximum electro-to-thermal conversion efficiency. |
表2 导电骨架复合相变材料性能Table 2 Properties of conductive framework phase change composites |
| Conductive framework | PCMS | Filler content (wt%) | Tm ( ℃) | Latent heat (J/g) | λ W/(m·k) | σ (S/m) | The trigger voltage (V) | η (%) | The working voltage(V) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| carbon foam | PEG6000 | - | 62.82 | 163.9 | - | - | - | 85 | 3.6 | 36 |
| carbon foam | paraffin wax | - | 57.05 | 120.2 | - | - | - | 74 | 3.6 | 36 |
| carbon foam | PU(PEG6000) | 33.3 | 43.2 | 61.9 | 0.48 | - | 0.8 | 75 | 1.1 | 37 |
| carbon fiber scaffold | paraffin wax | 15 | 39.22 | 182.22 | 0.424 | 19.6 | 2 | 81.1 | 3 | 38 |
| carbon aerogel | paraffin wax | 5 | 53.5 | 115.2 | - | 3.4 | - | 71.4 | 15 | 39 |
| cotton cloth/TPU | paraffin wax | 50.75 | 34.13 | 93.5 | - | 296.68 | 3 | 67.39 | 4 | 40 |
| CNT sponge | paraffin wax | 13 | 24 | 131.7 | 1.2 | - | 1.5 | 52.5 | 1.75 | 41 |
| CNT sponge | PU | 10 | 59.41 | 132.02 | 2.4 | - | 1.3 | 94 | 2 | 42 |
| CNT array | n-eicosane | 10 | 34 | 217.3 | - | - | 1 | 74.7 | 1.3 | 43 |
| single-wall CNT scaffold | eicosane | 27.1 | 36.7 | 204.8 | - | 620.3 | 3 | 80.1 | 4 | 44 |
| single-wall CNT scaffold | eicosane | 27.1 | 36.7 | 204.8 | - | 620.3 | 3 | 91.3 | 5 | 44 |
| graphite foam | Paraffin wax | 20 | 50.2 | 174.2 | 1.38 | - | - | 74.6 | 5 | 45 |
| graphite foam | PU(PEG4000) | 18 | 41 | 64.5 | 3.5 | - | - | 69 | 1.4 | 46 |
| graphite foam | PU(PEG6000) | 18 | 42.5 | 76.1 | 3.6 | - | - | 85 | 1.4 | 46 |
| graphite foam | PU(PEG8000) | 18 | 46.1 | 80.3 | 3.4 | - | - | 45 | 1.4 | 46 |
| graphite foam | PU(PEG6000) | 27 | 43.8 | 60.3 | 10.86 | - | 1.5 | 85 | 1.8 | 47 |
| graphite foam/MPU | octadecanol | 52.5 | 56.1 | 130 | 5.55 | - | - | 61.4 | - | 48 |
| graphite nanoplatelets | Pentaerythritol | 20 | 186 | 225.3 | 27 | 32 300 | 0.22 | 92.73 | 0.34 | 50 |
| 3D reduced graphene/ carbon scaffold | paraffin wax | 20 | 39.53 | 157 | 33.5 | 294.9 | - | 88 | - | 51 |
| 3D reduced graphene/ BN scaffold | PEG10000 | 15.2 | 59.5 | 164.1 | 0.59 | - | - | 87.9 | 7 | 52 |
| graphene aerogel | paraffin wax | 3 | 57 | 202.2 | 1.06 | - | - | - | - | 53 |
| graphene aerogel | Paraffin | 6 | 46.05 | 193.7 | 0.248 | 258.7 | 1 | 85.4 | 3 | 54 |
| graphene aerogel/ZnO | PU (PEG4000) | 2.29 | 57.1 | 108.1 | 2.99 | - | - | 84.4 | 15 | 55 |
| graphene aerogel/halloysite nanotubes | PU | 1.17 | 57.4 | 103.3 | - | - | 66.3 | 10 | 56 | |
| reduced graphene oxide aerogel/SEBS | paraffin wax | 6.47 | 40.19 | 226.3 | - | - | - | - | 8 | 57 |
| graphene nanoplatelets/ cellulose aerogel | PEG 6000 | 1.51 | 67.6 | 182.6 | 0.43 | - | - | - | - | 58 |
| graphene nanoplatelet/ cellulose nanofiber hybrid- coated melamine foam | PEG 6000 | 4.8 | 61.7 | 178.9 | 1.03 | 6.19 | - | 66.13 | 20 | 59 |
| MOF-derived carbon/ graphene oxide aerogel | lauric acid | - | 51 | 140 | 0.26 | - | 2.2 | 90 | 2.2 | 60 |
| ZIF@MOF-C/CNT | octadecane | 30 | 31.9 | 135.9 | 1.35 | 526.32 | - | 94.5 | 1.1 | 61 |
| copper nanowire aerogels | paraffin | 1.95 | 53 | 173.2 | - | 14 | - | - | - | 62 |
| CNTs nanoarray/nickel foam | 1-hexadecanamine | - | 50.38 | 132.2 | 0.277 | - | - | - | 30 | 63 |
| PEDOT:PSS/MXene framework | PEG20000 | 1.22 | 61.6 | 237.6 | 0.215 | 0.86 | - | - | 30 | 64 |
图4 (a)随机分布碳纳米管泡沫复合相变材料与电热转换[41];(b)定向排列碳纳米管阵列复合相变材料与电热转换[43]Fig. 4 (a) randomly distributed CNT sponge PCCs and its electrothermal conversion[41]. Copyright © 2012, American Chemical Society; (b) aligned CNT array PCCs and its electrothermal conversion[43]. Copyright © 2013, American Chemical Society |
表3 导电高分子复合电热相变材料性能Table 3 Properties of conductive polymer electrothermal phase change composites |
| Conductive polymer | PCMS | Filler content (wt%) | Tm ( ℃) | Latent heat (J/g) | λW/ (m·K) | σ (S/m) | The trigger voltage(V) | η (%) | The working voltage(V) | ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPy/crosslinked polystyrene | paraffin wax | - | 44.9 | 114.2 | - | 420 | 1.8 | 63.2 | 1.8 | 73 |
| PPy/crosslinked polystyrene | paraffin wax | - | 44.9 | 114.2 | - | 420 | 1.8 | 80.1 | 3 | 73 |
| PPy/ polydivinylbenzene nanotubes | paraffin wax | 27.1 | 30 | 145.7 | - | 55.6 | - | 66.8 | 2.2 | 74 |
| PPy/ polydivinylbenzene nanotubes | paraffin wax | 27.1 | 30 | 145.7 | - | 55.6 | - | 89.6 | 2.5 | 74 |
| PPy/Cellulose nanofiber | PEG | 6 | 57.41 | 169.7 | - | - | 1.75 | 76.6 | 1.75 | 75 |
| PPy/Cellulose nanofiber | PEG | 6 | 57.41 | 169.7 | - | - | 1.75 | 85.1 | 1.9 | 75 |
| PPy/melamine- formaldehyde | n-octadecane | 50.3 | 30 | 90.2 | - | 0.33 | - | - | - | 76 |
| PPy/PU | PEG | 60.8 | 47.5 | 62.8 | - | 1184 | - | - | - | 77 |
图5 (a)电热相变材料的应用;(b)电热相变材料应用示意图;电热相变材料用于(c)电池温度管理和(d)人体保温[28]Fig. 5 (a) Application of electrothermal PCCs, (b) Application mode of electrothermal PCCs, (c) Temperature change of battery with or without electrothermal PCCs, (d) PCCs for human thermal insulation[28]. Copyright ©#x00A9; 2022, American Chemical Society |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5: 755.
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |